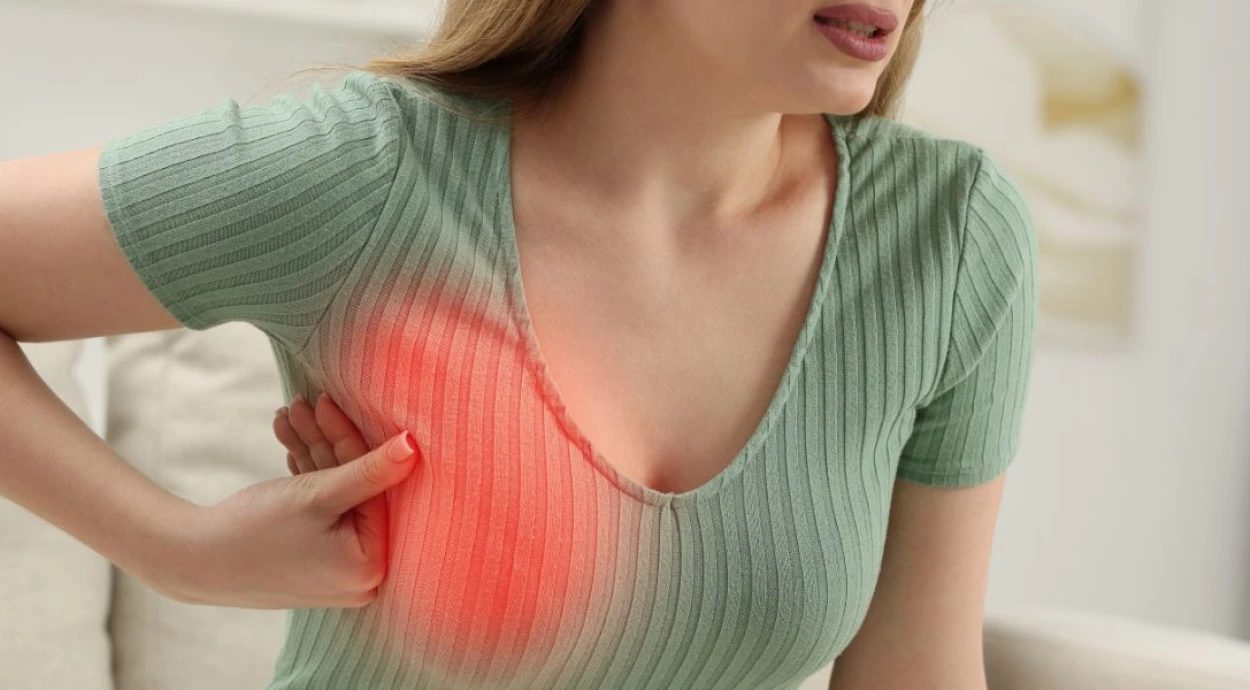
Any changes that occur in the breasts can cause concern, especially if they are accompanied by pain or lumps. One of the common benign diseases is diffuse fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands. This pathology is characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue in the glands and may be accompanied by pain and changes in the structure of the breast.
In this article, we will consider the main causes of fibroadenomatosis, its symptoms, diagnostic and treatment methods, as well as explain how to prevent its development.
What Is Diffuse Fibroadenomatosis of the Mammary Glands?
Fibroadenomatosis is a benign disease of the mammary glands that belongs to mastopathies (benign changes in the mammary glands accompanied by the proliferation of connective and glandular tissue). It is accompanied by uneven proliferation of connective and glandular tissue, which leads to lumps, pain, and changes in the breast structure.
In the diffuse form of fibroadenomatosis, pathological processes spread evenly throughout the breast tissue. This distinguishes it from the nodular form, in which separate lumps occur. The disease is more common in women of reproductive age and is associated with hormonal changes in the body.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diffuse Fibroadenomatosis
The main cause of fibroadenomatosis is hormonal imbalance. A disruption in the ratio of estrogen and progesterone affects the breast tissue, causing hyperplasia.
Risk factors include:
-
Hormonal disorders. A high level of estrogen or deficiency of progesterone promotes connective tissue growth.
-
Gynecological diseases. Inflammatory processes, polycystic ovary syndrome, and uterine fibroids can cause hormonal imbalance.
-
Stress and psychoemotional overload. Prolonged nervous strain affects the functioning of the endocrine system.
-
Genetic predisposition. If the mother or grandmother had mastopathies, the risk of their occurrence in subsequent generations is higher.
-
Poor nutrition. Excess fatty food, fast food, and vitamin deficiency can negatively affect hormonal balance.
-
Thyroid diseases. Deficiency or excess of thyroid hormones may cause disorders in the mammary glands.
Symptoms of Fibroadenomatosis
The signs of the disease may vary depending on the stage and individual characteristics of the body. The main symptoms are:
-
breast pain (mastalgia), which worsens before menstruation;
-
lumps in the breast tissue;
-
increased breast sensitivity;
-
swelling of the mammary glands;
-
nipple discharge (clear, yellowish, or with blood traces);
-
discomfort when touched or pressed.
Symptoms may disappear after menstruation, but as the disease progresses, the pain becomes constant.
Types of Diffuse Fibroadenomatosis
Diffuse fibroadenomatosis may have different forms, which differ by the nature of changes in breast tissue. The main types of this pathology include:
-
Mild diffuse fibroadenomatosis. The initial form of the disease, in which minor changes occur in the tissues. Symptoms may be weakly expressed, and pain occurs only periodically, more often before menstruation.
-
Diffuse fibroadenomatosis with cystic component. Characterized by the formation of small or medium cysts filled with fluid. This may be accompanied by more pronounced pain, a feeling of fullness, and breast discomfort.
-
Diffuse fibroadenosis of the mammary glands. In this form, the proliferation of connective tissue prevails, leading to lumps but without distinct nodes or cysts. This condition may cause uneven tissue density and increased breast sensitivity.
Each type of lesion requires thorough diagnosis and monitoring, as symptoms may worsen over time. Timely detection and correction of hormonal balance help control fibroadenomatosis and prevent complications.
Diagnosis of Diffuse Fibroadenomatosis
The following methods are used to establish the diagnosis:
-
Examination and palpation of the breasts. The doctor evaluates the tissue structure, presence of lumps, and sensitivity.
-
Ultrasound (US). Helps to detect diffuse changes and cystic formations.
-
Mammography. X-ray examination allows assessing the condition of the breasts in women over 40 years.
-
Biopsy. If atypical cells are suspected, tissue examination is performed.
-
Hormonal tests. Allow assessing the level of estrogens, progesterone, and prolactin.
Treatment Methods
Treatment of fibroadenomatosis of the breasts depends on the degree of disease development, the nature of tissue changes, and the general condition of the body. The main therapeutic measures are aimed at normalizing the hormonal balance, relieving pain, and preventing progression.
1. Conservative Treatment
Conservative methods are the main approach since the disease is not oncological and does not require surgery. The main directions of such treatment:
Hormone therapy
Since fibroadenomatosis is associated with sex hormone imbalance, it is important to restore their normal level. For this purpose, the following are used:
-
progesterone drugs – to compensate for progesterone deficiency and reduce estrogen influence;
-
anti-estrogen drugs – to block the excessive effect of estrogen on breast tissue;
-
oral contraceptives – to regulate the menstrual cycle and stabilize hormonal balance;
-
gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists – in cases of severe hormonal imbalance.
Hormone therapy is prescribed only by a doctor after hormone level tests, as self-administration may worsen the condition.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Used to reduce pain and inflammatory manifestations in the breasts. They help relieve swelling and discomfort, especially in the premenstrual period.
Phytotherapy and vitamin complexes
Herbal preparations and vitamins play an important role in maintaining hormonal health. Usually recommended:
-
B vitamins – improve the nervous system and reduce stress effects;
-
vitamin E – has antioxidant properties and positively affects breast tissue;
-
iodine-containing drugs – normalize thyroid function, important for hormonal balance;
-
magnesium – reduces irritability and improves the nervous system, helping to reduce mastalgia.
Herbal remedies can be used as an additional method in complex treatment.
2. Lifestyle Correction and Diet Therapy
Nutrition and lifestyle play an important role in hormonal regulation and may influence fibroadenomatosis development. Recommendations include:
-
limiting coffee, alcohol, chocolate, and fatty food, as they may intensify pain and affect estrogen metabolism;
-
increasing fiber intake (vegetables, fruits, grains) to normalize digestion and remove excess estrogen;
-
consuming healthy fats (avocado, nuts, fish) to support hormonal balance;
-
regular physical activity to improve blood circulation and metabolic processes;
-
weight control, since excess weight may contribute to higher estrogen levels.
3. Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures help reduce pain, improve blood circulation in the breasts, and decrease inflammation. Effective methods include:
-
electrophoresis with medications (iodine, magnesium) – promotes resorption of lumps;
-
magnetotherapy – improves blood circulation and reduces tissue swelling;
-
laser therapy – has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Physiotherapy may be used as an auxiliary method along with drug therapy.
4. Surgical Treatment
In most cases, surgery is not needed for diffuse fibroadenomatosis, as it is a benign pathology. However, surgical intervention may be required if:
-
suspicious nodular formations are detected that require biopsy;
-
severe pain is not relieved by conservative treatment;
-
cysts reach significant size and cause discomfort.
In such cases, sectoral resection (removal of the affected breast area) or cyst puncture with fluid aspiration may be performed.
5. Dispensary Monitoring
Women diagnosed with diffuse fibroadenomatosis are advised to undergo regular check-ups with a mammologist, even if symptoms are absent. This allows controlling breast condition and detecting possible changes in time.
Treatment of diffuse fibroadenomatosis requires a comprehensive approach, including drug therapy, lifestyle correction, physiotherapy, and regular medical monitoring. Timely medical consultation and adherence to recommendations help reduce symptoms, prevent complications, and maintain breast health.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of fibroadenomatosis, it is important to:
-
undergo regular mammologist check-ups;
-
maintain hormonal balance;
-
avoid stress;
-
follow a healthy diet;
-
monitor thyroid function;
-
lead an active lifestyle.
Timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment help prevent complications and improve a woman’s quality of life.
If you experience discomfort in your breasts or notice changes in their structure, it is important not to ignore these symptoms. Diffuse fibroadenomatosis is a benign disease that, with timely diagnosis and proper treatment, does not pose a threat to health.
To receive professional consultation and undergo the necessary examinations, contact the experienced mammologists of the Oxford Medical Center in Kyiv. Appointments are available at a convenient time – take care of your health today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is diffuse fibroadenomatosis with a cystic component?
This is a form of fibroadenomatosis accompanied by the proliferation of connective tissue and the formation of small cysts filled with fluid. The disease may cause pain, swelling, and discomfort in the breasts, especially before menstruation. It is diagnosed using ultrasound and mammography.
How to distinguish fibroadenomatosis from other breast pathologies?
Fibroadenomatosis has a diffuse nature of tissue changes, while, for example, fibroadenoma is a separate node. It differs from mastitis by the absence of pronounced inflammation. Ultrasound, mammography, and cytological examination help establish the exact diagnosis and exclude oncological processes.
Can diffuse fibroadenomatosis be treated conservatively?
In most cases, treatment is possible without surgery. Hormone therapy, vitamins, herbal remedies, diet therapy, and physiotherapy are used. Lifestyle correction also helps reduce symptoms. It is important to undergo regular check-ups with a mammologist to control breast condition. However, these methods only help to control the tumor and reduce the risk of its growth. The tumor can be removed only surgically.