Table of Contents
- What Is Laparoscopy in Gynecology
- Key Indications for Laparoscopic Gynecologic Surgery
- Laparoscopy in the Treatment of Infertility and Endometriosis
- How Laparoscopic Surgery Is Performed
- Benefits of Laparoscopy for Patients
- Contraindications and Possible Limitations
- What to Expect After Surgery: Rehabilitation and Recovery
- Gynecologic Laparoscopy at «Oxford Medical»
- Frequently Asked Questions
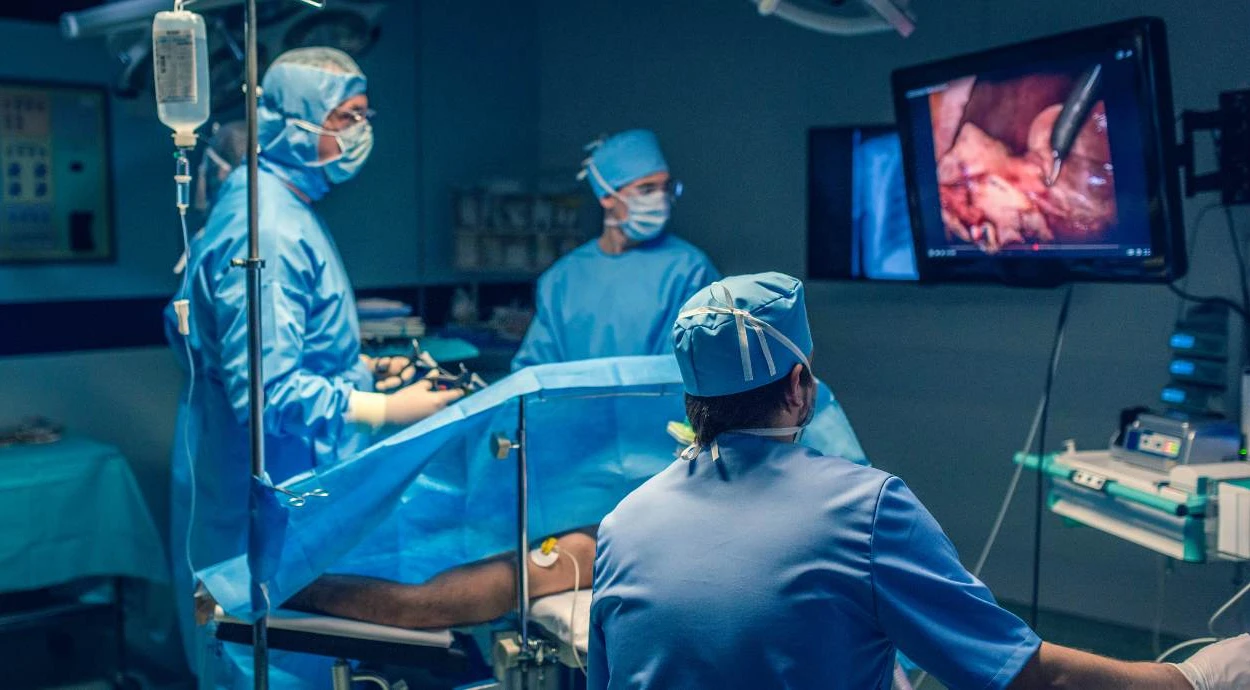
Laparoscopy in gynecology is a modern minimally invasive surgical method. During laparoscopic surgery, the doctor makes several small punctures in the abdominal wall, usually up to 1 cm, through which surgical instruments and an optical camera are inserted. The image from the camera is displayed on a monitor in a magnified view, providing precise control at every stage of the procedure.
With this visualization, the doctor can assess the pelvic organs in detail and perform manipulations as carefully as possible without injuring healthy tissues. This precision is one of the key advantages of laparoscopy compared to open surgery, where a large incision is made.
For the patient, laparoscopy means less surgical trauma, a lower level of postoperative pain, and faster recovery. Small punctures are sutured and heal much more quickly, while the risk of complications and the formation of prominent scars is significantly reduced. That is why laparoscopic techniques are now widely used in gynecology to treat many conditions and are considered one of the most gentle surgical approaches.
What Is Laparoscopy in Gynecology
Modern surgical gynecology actively uses laparoscopic methods, as they allow achieving high precision of intervention with minimal tissue trauma.
Laparoscopy can be used both for planned operative treatment and for уточнення діагнозу with the possibility to perform the necessary intervention immediately.
Unlike open surgery, laparoscopy does not require a large abdominal incision, which fundamentally changes the approach to surgical treatment.
A key feature of the method is the use of a laparoscope — a thin optical device with a camera and a light source. It allows the doctor to see internal organs in a magnified view and with high clarity. This is important not only for precise movements, but also for correctly assessing the extent of the pathological process, the condition of tissues, and the anatomical relationships between structures.
In gynecology, laparoscopy is used as:
- a diagnostic method when it is necessary to clarify the cause of symptoms or confirm a diagnosis;
- a therapeutic method when, during the procedure, pathological formations are removed or other necessary manipulations are performed.
It is important to note that laparoscopy is not a “light” version of surgery. It is a full-fledged surgical intervention performed for clear indications, with all safety requirements observed and under general anesthesia. At the same time, due to the technical capabilities of the method, high precision can be achieved with minimal injury to healthy tissues.
Key Indications for Laparoscopic Gynecologic Surgery
.jpg)
Laparoscopy in gynecology is used when surgical intervention is required, but it can be performed in the most tissue-sparing way possible.
Most commonly, laparoscopic surgery is indicated for:
- ovarian cysts and benign ovarian masses;
- endometriosis of various localizations;
- uterine fibroids (if the nodes are of appropriate size, laparoscopic myomectomy is performed);
- pelvic adhesions;
- chronic pelvic pain of unclear origin;
- suspected fallopian tube pathology;
- certain forms of female infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy (when the patient is clinically stable).
It is important to understand that the presence of indications does not automatically mean laparoscopy will be chosen. The final decision is made by the doctor after a full evaluation, risk assessment, and an estimate of the expected effectiveness of this method for the specific patient.
Laparoscopy in the Treatment of Infertility and Endometriosis
Laparoscopy plays an important role in treating conditions that directly affect a woman’s reproductive health. In particular, the laparoscopic approach is widely used in infertility and endometriosis when it is necessary not only to confirm pathology, but also to eliminate its causes as gently as possible.
In infertility, laparoscopy makes it possible to assess the condition of the pelvic organs, fallopian tubes, and ovaries in cases where non-invasive examinations do not provide a complete picture. During surgery, the doctor may identify adhesions, endometriotic lesions, or anatomical features that prevent pregnancy and can perform the necessary interventions immediately. This approach helps reduce the number of separate procedures and shortens the overall treatment pathway.
Laparoscopy is also one of the key methods of surgical treatment for endometriosis. Due to precise visualization, even small lesions can be detected and removed with minimal trauma to healthy tissues. This is especially important for preserving the function of the ovaries and fallopian tubes and for reducing the risk of recurrence.
How Laparoscopic Surgery Is Performed
.jpg)
Laparoscopic surgery is performed in an operating room setting, following all safety standards, and under general anesthesia. Before the procedure, the patient undergoes the necessary examinations that allow the doctor to plan the scope of surgery and assess potential risks.
During surgery, several small punctures are made in the anterior abdominal wall. A laparoscope with a camera and surgical instruments are inserted through these access points. The surgical field is displayed on a monitor in a magnified view, enabling the doctor to clearly see anatomical structures and work with high precision.
The sequence of steps during laparoscopic surgery depends on the clinical situation and the goals of the procedure. After all manipulations are completed, the instruments are removed, the puncture sites are sutured, and sterile dressings are applied.
The duration of surgery depends on its complexity and extent. Due to minimal tissue trauma, patients typically tolerate this procedure better than open surgery, and recovery is faster.
Benefits of Laparoscopy for Patients
The main advantage of laparoscopy is the ability to provide full surgical treatment with minimal tissue intervention. This directly affects both the course of surgery and the patient’s well-being during the postoperative period.
The key benefits of laparoscopic surgery include:
- less tissue trauma because the procedure is performed through small punctures rather than a large incision;
- less pronounced postoperative pain, reducing the need for analgesics;
- faster recovery compared to open surgery and a shorter hospital stay;
- lower risk of postoperative complications, including infections and adhesions;
- better cosmetic outcome, as puncture sites usually leave minimal or almost invisible marks after healing.
In addition, due to precise visualization of the surgical field, laparoscopy allows the doctor to act more accurately and carefully, minimizing injury to healthy tissues. This is especially important in gynecology, where preserving reproductive function is often a key objective.
Contraindications and Possible Limitations
Despite the broad possibilities of laparoscopy, this method is not suitable for every patient. The choice of surgical approach is always based on an individual assessment of health status, the nature of the condition, and potential risks.
Absolute contraindications include conditions in which laparoscopy is unsafe, such as severe cardiovascular or respiratory disorders that make general anesthesia impossible, as well as critical situations requiring immediate open surgery.
Relative limitations also exist, where the possibility of laparoscopy is determined individually. These may include extensive adhesions, large neoplasms, a history of complex abdominal surgeries, as well as certain comorbidities.
It is important to understand that the presence of limitations does not always mean laparoscopy must be ruled out. In many cases, the decision is made after additional examinations and consultations, weighing the benefits against possible risks. The final treatment strategy is determined by the doctor, focusing on safety and effectiveness for the specific patient.
What to Expect After Surgery: Rehabilitation and Recovery
Recovery after laparoscopic surgery is typically easier than after open surgery. This is due to minimal tissue trauma and the absence of a large abdominal incision.
Hospitalization after laparoscopy is usually short. In most cases, the patient stays in the hospital for 1 to 3 days, depending on the scope of the procedure and overall condition. As early as the first day after surgery, patients are usually allowed to get up, move independently, and gradually return to normal activity.
Diet after laparoscopy is restored gradually. During the first day after surgery, depending on well-being, light food is recommended. Later, the diet is expanded, with an emphasis on foods that are easy to digest and do not cause bloating or discomfort. A full diet is usually possible within a few days.
In the first days after surgery, moderate pain at the puncture sites, pulling sensations in the lower abdomen, general weakness, or fatigue may occur. These symptoms are typical after surgery and usually decrease gradually over several days.
During recovery, the patient is usually advised to:
- limit physical activity and avoid heavy lifting for the period defined by the doctor;
- gradually increase activity, avoiding sudden movements and overexertion;
- follow a gentle diet during the first days after surgery;
- drink enough fluids;
- take medications prescribed by the doctor;
- maintain an appropriate rest regimen;
- attend follow-up appointments at scheduled times.
The duration of rehabilitation and detailed recommendations depend on the scope of laparoscopic intervention and individual characteristics. Following the doctor’s guidance helps ensure safe recovery and reduces the risk of possible complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is pregnancy possible after laparoscopic surgery?
In many cases, pregnancy after laparoscopic interventions is not only possible but may become more likely. This is because laparoscopy is a procedure during which factors that previously prevented conception—such as adhesions or endometriosis lesions—can be eliminated. The final prognosis depends on the reason for surgery and individual characteristics.
How long should physical activity be restricted after surgery?
The duration of restrictions depends on the scope of the procedure. In most cases, light activity is allowed within the first days, while intensive exercise and sports are usually limited for several weeks. Specific timeframes are determined by the doctor during postoperative follow-up.
Can pregnancy be planned immediately after laparoscopy?
Pregnancy planning is possible only after the recovery period has been completed. In some cases, the doctor may recommend waiting several months to allow the body to fully recover. Optimal timing is always determined individually, taking into account the goal and extent of the surgery.
Will there be scars after laparoscopy?
After laparoscopy, only small marks from the punctures remain, which typically become barely noticeable over time. Because there is no large incision, the cosmetic outcome is significantly better than after open surgery and usually does not cause aesthetic discomfort.
Does laparoscopy affect sexual life?
After recovery is complete, laparoscopic surgery generally does not have a negative impact on intimate life. On the contrary, eliminating pain or other symptoms may improve overall well-being. The timing for returning to sexual activity is determined by the doctor depending on the course of rehabilitation.
What is diagnostic laparoscopy?
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a surgical method that allows the doctor to directly examine the pelvic organs in cases where other diagnostic methods do not provide sufficient information. If needed, it can be converted into a therapeutic procedure within the same operation.
Can laparoscopy be combined with other treatments?
Yes, laparoscopic intervention is often part of a comprehensive treatment plan. It may be combined with medication therapy, hormonal treatment, or subsequent reproductive medicine programs, depending on the diagnosis and treatment goals.




.jpg)