The information in the article is provided for reference only and is not a guide to self-diagnosis or treatment. If symptoms of a disease occur, you should consult a doctor.
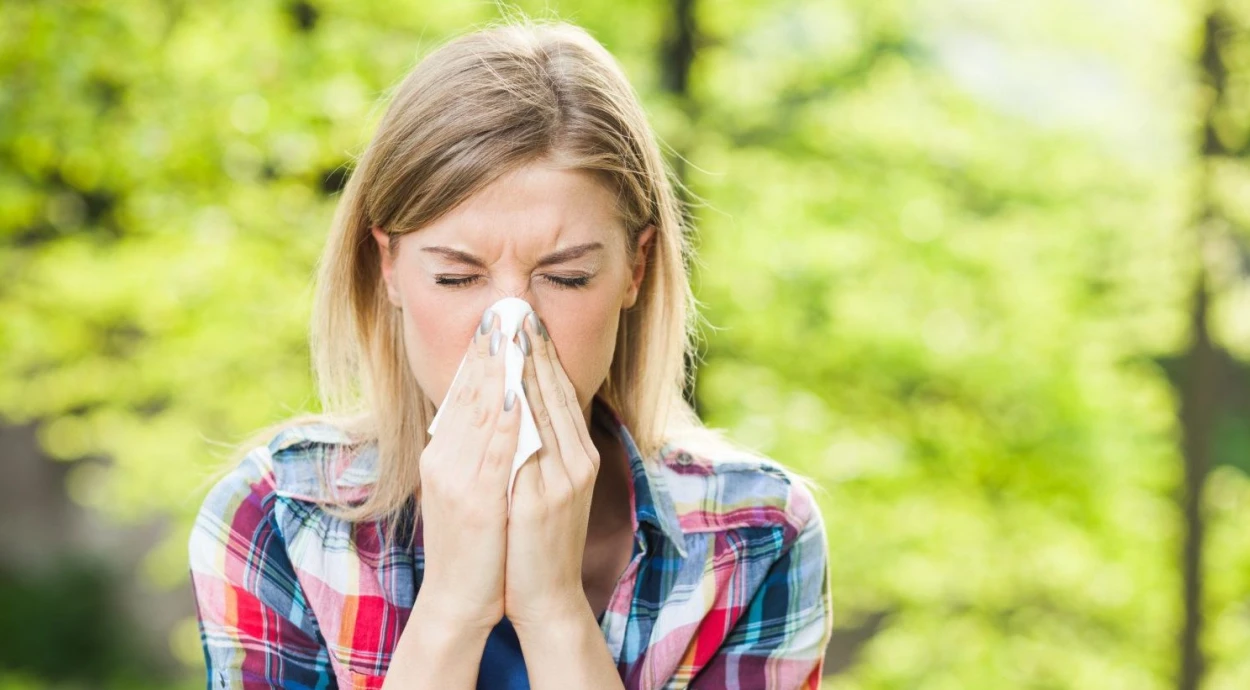
Most people are familiar with allergies in one way or another. Some experience them rarely, while for others they cause discomfort almost constantly. Allergy is a specific reaction of the immune system to a certain substance (allergen) that enters the body or contacts the skin. Most often it manifests as sneezing, runny nose, tearing, itching, and skin rashes. Allergy is not a natural but a hypersensitive reaction of the body.
How does allergy develop?
Allergy often develops in response to contact with an allergen. It can be any foreign substance that the immune system mistakenly identifies as potentially dangerous and therefore tries to neutralize as quickly as possible. As a result, the body triggers the production of specific antibodies (immunoglobulins of class E) aimed at destroying this particular allergen. This and related processes lead to the development of allergy symptoms.
The development of allergy is associated with the process of sensitization – a gradual increase in hypersensitivity to a particular substance. Thus, allergy symptoms may not appear at the first contact with the allergen, but later. The sensitization period can last from several days or weeks to several years. At the same time, the allergic reaction to the allergen may become stronger over time.
Allergy symptoms
The most common allergy symptoms are watery eyes, nasal congestion, and sneezing. However, it can also manifest differently depending on the type of allergen and the way of contact with it.
Allergy symptoms may include:
-
frequent and strong sneezing;
-
profuse watery nasal discharge;
-
itching in the nose;
-
tearing;
-
redness of the eyes and itching;
-
dry cough, shortness of breath, chest tightness;
-
redness and swelling of the skin;
-
localized or widespread skin rashes;
-
skin flaking;
-
swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, and throat, as well as lips, face, and neck;
-
abdominal pain;
-
nausea, vomiting;
-
diarrhea and others.
When allergens enter the respiratory tract, sneezing, nasal congestion, and similar symptoms usually occur. If the allergen comes into contact with the skin (for example, animal hair or detergent), redness and rash may appear. When consuming products that cause allergies, nausea, vomiting, and swelling of the mucous membranes are possible.
Allergy symptoms are similar to those of other diseases. Most often it is confused with a cold or viral infection. To determine the exact cause, diagnosis is required.
How to distinguish allergy from a cold and other diseases?
Only an experienced doctor can make the correct diagnosis. At the same time, the doctor needs to carefully study the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and test results. However, it is possible to assume whether the symptoms are manifestations of an allergy or an acute illness based on certain signs:
-
Allergy symptoms appear more sharply than cold symptoms. They may occur when going outdoors (pollen allergy), being in a polluted room, contact with a cat or other pet, eating certain foods, etc. Cold symptoms usually develop gradually, increasing over time.
-
Cold symptoms may worsen in the cold, while allergy symptoms worsen with repeated contact with the allergen.
-
With allergy, nasal discharge is usually abundant and watery, while with a cold it is thicker, yellow, or greenish.
-
Acute illness symptoms usually decrease and disappear within 5–14 days. Allergy may go away faster or, on the contrary, last for months with constant exposure to the allergen.
-
Allergy reactions are not usually accompanied by fever, while colds and viral diseases most often cause it.
-
Sore throat, headache, muscle pain, chills, and general weakness are also more typical for colds.
-
Allergy is more often characterized by tearing, itching in the eyes and nose.
-
Allergy may be seasonal, for example, developing every year at the same time.
Causes of allergy in children and adults
The cause of allergy is an inadequate response of the immune system to a substance that is safe for the body. It can be food, plant pollen, household dust, animal hair, or something else.
Among the main causes of such a body reaction, the hereditary factor plays a key role. Scientists have found that if one parent has an allergy to certain substances, the likelihood of its occurrence in a child is 33%, and if both parents – 70%. Living conditions and the environmental situation in the region where a person lives are also of great importance. According to statistics, residents of cities in developed countries suffer more from allergies. This is associated with less contact with potential allergens.
The main causes of allergy are considered to be:
-
hereditary predisposition;
-
weakened immunity;
-
unfavorable environmental situation;
-
poor diet;
-
frequent stress and fatigue;
-
constant use of medications;
-
frequent colds and viral diseases;
-
artificial feeding in infancy.
However, today these causes are only considered probable.
What can cause allergy?
A wide variety of factors can trigger an allergic reaction. They are individual for each person.
Allergy can be caused by:
-
plant pollen;
-
household dust;
-
animal hair and saliva;
-
insect bites;
-
mold and fungi spores;
-
food;
-
medications;
-
cosmetics, hygiene products, and household chemicals;
-
latex and synthetic fabrics.
It is important to consider that even a small dose of allergen can cause a severe allergic reaction. For example, in case of nut intolerance, it is dangerous to consume dishes containing even a few grams of this product.
It is advisable to track what causes the allergy and avoid contact with these substances at least until treatment is carried out.
Allergy diagnosis
An allergist can help identify what causes the allergy and select the optimal treatment. During the initial consultation, the specialist asks in detail about the symptoms, their severity, and the moment of onset. The doctor also studies the medical history and asks whether close relatives have allergies.
During the examination, the allergist pays attention to the condition of the eyes, throat and nasal mucous membranes, as well as the skin. If characteristic signs are present, the doctor can confirm an allergic reaction. But to make an accurate diagnosis and identify allergens, diagnostics are necessary.
The main diagnostic methods are:
-
provocation skin tests;
-
blood tests for antibodies – immunoglobulins E.
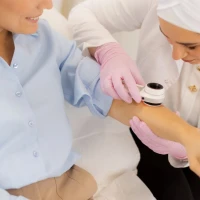
Skin tests are tests in which small doses of suspected allergens are introduced into the body. They are mainly performed in two ways: small scratches are made on the forearm skin and drops of the substance are applied, or it is injected under the skin with an injection. If a person is allergic, the skin at the contact site becomes red and slightly swollen.
Allergy can also be detected by a blood test for the presence of allergen-specific immunoglobulins E. This method is used less frequently. Usually, tests are prescribed as an additional diagnostic method or if skin tests cannot be performed.
Allergy treatment methods
Allergy treatment has two goals:
-
elimination of symptoms;
-
reducing the severity of the allergic reaction upon contact with the allergen.
In the first case, a set of medications is prescribed to reduce the manifestation of symptoms. Initially, antihistamines are used, which block the synthesis of histamine. It is produced in response to the allergen entering the blood and causes a deterioration in well-being. At the same time, the doctor may prescribe nasal vasoconstrictor drops to eliminate runny nose and other drugs.
To reduce the allergic reaction and the risk of complications, immunotherapy is prescribed. This is a long-term treatment involving the regular administration of special doses of allergens. Thanks to this, the body gradually gets used to them and stops reacting violently. Such treatment is necessarily carried out under the supervision of an allergist. Injections are given in the clinic, after which the patient remains there for some time (usually 30–60 minutes).
It is not recommended to take allergy medications independently or use them longer than prescribed by the doctor. The body may develop resistance to antihistamines and vasoconstrictor drugs, reducing their effectiveness.
Why is allergy dangerous and why treat it?
The most dangerous complication of allergy is anaphylactic shock. This is an acute reaction of the body to an allergen. It may manifest as swelling and spasm of the respiratory tract muscles. Anaphylaxis can also cause headache, loss of consciousness, seizures, involuntary urination, and myocarditis.
Symptoms of anaphylactic shock include sudden sweating, shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air, headache, chest pain, low blood pressure, and loss of consciousness. In this case, the person needs emergency medical care, as life-threatening conditions may occur.
Other complications of allergy may include diseases of the nose and respiratory tract, including asthma. According to research, allergy is the cause of asthma development in children in 90% of cases and in adults – in 50%. Atopic dermatitis, eczema, and some other diseases may also develop against the background of allergy.
Contrary to the common belief that the body gradually gets used to allergens, in fact the opposite happens. With repeated contact with allergens, the reaction becomes more pronounced, which can lead to complications. Therefore, it is so important to consult a doctor in time and undergo treatment.
Allergy prevention
To prevent allergic reactions, it is recommended to minimize contact with allergens. For this, provocation tests can be performed to determine what the body reacts to. If these are food products, cosmetics, or household chemicals, it is better to avoid them. In case of allergy to animal hair or saliva, it is advisable not to stay with them in the same room. If the body does not tolerate household dust, it is necessary to do wet cleaning more often and do it while wearing a protective mask and gloves. Bedding (blankets and pillows) can also be replaced with hypoallergenic ones.
Immunological treatment is also considered a method of allergy prevention. It allows the body to gradually adapt to certain substances and reduce the risks from contact with them.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms of allergy?
Most often, allergy causes tearing, profuse watery nasal discharge, itching in the nose and eyes, frequent sneezing. When an allergen contacts the skin, red spots, rashes, itching, and peeling may appear. Rarer symptoms include swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat, cough, nausea, vomiting, and others.
What types of medications are prescribed for allergy?
To relieve allergy symptoms, antihistamines are used. For treatment, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics and a course of immunotherapy or other drugs prescribed by an allergist.
What are the main types of allergy?
The main types of allergy are reactions to flower and plant pollen, household dust, animal hair, food, medications, cosmetics, and household chemicals.
Related services:
Allergology
Sources:
European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Journal of Clinical Immunology and Allergy