Contents:
- What is nail fungus (onychomycosis)
- What nail fungus looks like
- How to identify fungus on fingernails and toenails
- Causes of nail fungus
- How to treat nail fungus
- Prevention of reinfection with nail fungus
A change in the color of the nail plate, its thickening, brittleness, or the appearance of spots — is not only a cosmetic defect, but also a possible sign of an infectious lesion. Most often, the cause of such changes is a fungal infection, which requires timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment.
Many people postpone seeing a doctor, hoping that the problem will go away on its own. However, fungal nail infection usually progresses slowly but persistently, spreading to neighboring nails and surrounding tissues. The earlier the changes are detected and the diagnosis is confirmed, the higher the chances of full restoration of the nail plate without complications.
In this article, we will take a detailed look at how to identify nail fungus, which symptoms are typical for early and advanced forms, which diseases it can be confused with, and which modern approaches are used for treatment.
What is nail fungus (onychomycosis)
Nail fungus, or onychomycosis — is an infectious lesion of the nail plate caused by fungal microorganisms. They multiply in the tissues of the nail and gradually disrupt its normal structure and growth.
Most often, the disease is caused by dermatophytes. Less often, the cause may be yeast or mold fungi. The type of pathogen matters for selecting treatment, so if necessary, the doctor prescribes a laboratory test.
Onychomycosis is a contagious disease. The infection can be transmitted through close contact or through shared household items, in particular towels, shoes, or manicure tools.
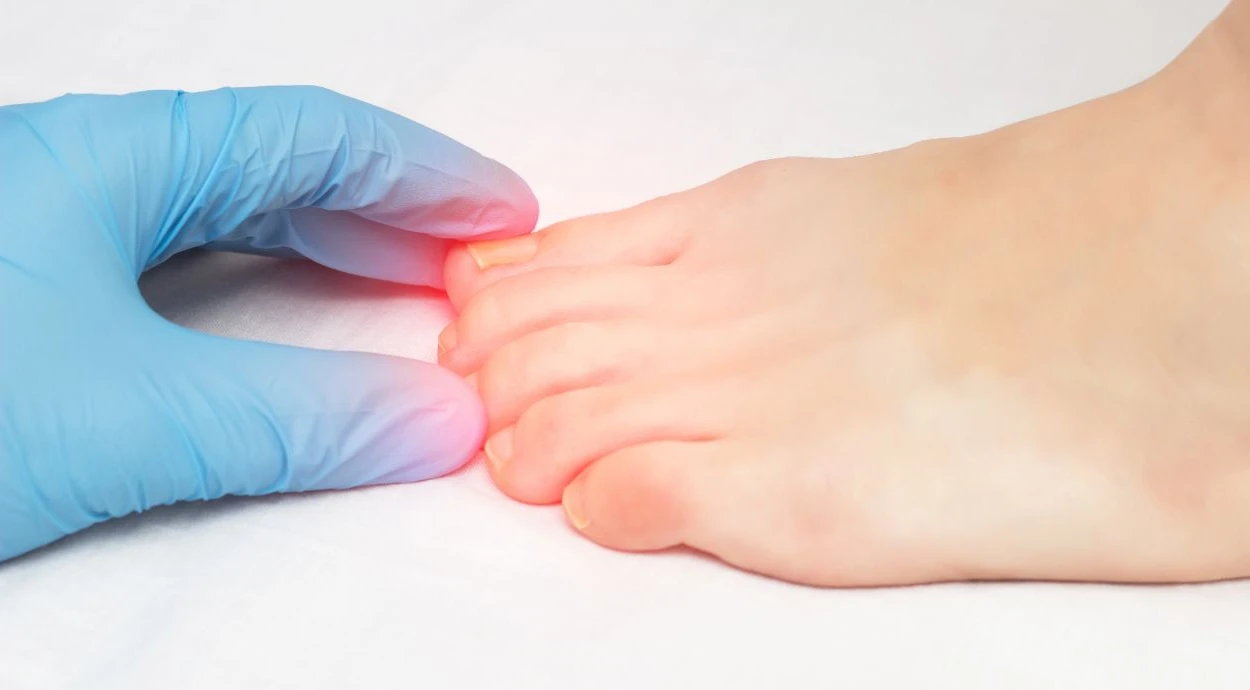
What nail fungus looks like
External changes in fungal infection may differ depending on the stage of the process, the depth of the lesion, and individual characteristics of nail growth. At the beginning, the changes are often barely noticeable, but over time they become more pronounced and affect not only the color, but also the shape and density of the nail plate.
To suspect the problem in time, it is important to know which manifestations are characteristic of different stages of infection development.
Early signs of nail fungus
At an early stage, a fungal infection usually does not cause pain, so a person may not pay attention to the changes for a long time. Most often, a small spot of whitish, yellowish, or grayish color appears, located near the edge of the nail or on the side.
Early manifestations also include:
- loss of the nail’s natural shine;
- appearance of thin streaks or pinpoint spots;
- slight splitting of the free edge;
- minor thickening of a separate area.
The nail plate still retains its shape, and the changes may resemble the consequences of an injury.
Advanced nail fungus: characteristic changes
Without treatment, the infection gradually affects a larger part of the nail plate. The color becomes more intense — yellow, brown, or even dark brown. The nail plate thickens, becomes uneven, brittle, and may deform.
The advanced form is characterized by:
- pronounced thickening of the nail;
- crumbling and brittleness;
- partial detachment from the nail bed;
- unpleasant odor when toenails are affected;
- discomfort or pain when pressed.
In some cases, the nail changes shape significantly, becoming wavy or curved.
Differences between toenail and fingernail fungus
.jpg)
Fungal infection can develop on both the hands and the feet, however, the course has certain differences. On the feet, the infection is much more common due to increased moisture and tight shoes.
For toenails, the following are more characteristic:
- pronounced thickening of the plate;
- slow but deep involvement;
- involvement of several nails at the same time.
On the hands, fungus usually manifests sooner with noticeable color changes and splitting, but thickening may be less pronounced. Often one or two nails are affected.
Regardless of the location, any persistent changes in the structure or color of the nail require evaluation by a specialist. Visual signs may be similar to other diseases, so an accurate diagnosis is established after an examination and, if necessary, laboratory confirmation.
How to identify fungus on fingernails and toenails
Visual changes may be alarming, but an examination alone is not enough to confirm the diagnosis. To accurately determine whether the lesion is fungal, it is important to assess the combination of symptoms, the duration of the process, and the results of the examination.
The algorithm of actions when fungal infection is suspected includes:
- clinical examination of the nails;
- assessment of the condition of the surrounding skin;
- medical history taking (injuries, visiting a swimming pool, wearing tight shoes);
- laboratory examination of a scraping from the nail plate.
It is laboratory confirmation that makes it possible to distinguish a fungal infection from other dermatological conditions and to select effective therapy.
How to recognize fingernail fungus
On the hands, changes are usually noticed earlier because the nails are exposed and a person pays attention to their appearance sooner. Persistent changes that do not disappear after removing decorative coating or after care should be a concern.
Signs that require a doctor’s consultation are:
- color change without a prior injury;
- uneven density of the nail plate;
- gradual spread of changes to other nails;
- combination with peeling of the skin of the hands.
It is important to consider that frequent use of gel polish or aggressive products can mask or imitate the problem, so it is difficult to determine the cause on your own.
How to identify toenail fungus
On the feet, the infection is often detected later because the nails are hidden by shoes. A person may notice the problem only when the changes become pronounced.
A reason to see a doctor is:
- persistent thickening of the nail that makes trimming difficult;
- gradual involvement of several nails;
- combination with itching or cracks between the toes;
- recurrence of changes after a short-term «improvement».
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor performs an examination and takes material for microscopic or culture testing. This makes it possible to establish the exact cause of the changes and determine the treatment strategy.
Which diseases nail fungus is confused with
Not all changes in the nail plate are fungal in nature. There are conditions that may look similar but require a completely different approach to treatment.
Most often, fungal infection is confused with:
- nail psoriasis;
- traumatic dystrophy;
- consequences of chemical damage;
- bacterial infection;
- congenital features of nail structure.
That is why making a diagnosis «by eye» can be mistaken. If the changes persist or progress, it is advisable to consult a specialist who will conduct the necessary examination and determine the cause of the disorders.
Causes of nail fungus
For an infection to develop, a combination of two conditions is necessary: contact with the pathogen and a favorable environment for its reproduction. Not every person develops the disease after contact with fungus — the condition of the skin, nails, and overall immunity plays an important role.
Main routes of infection
Most often, infection occurs in places with high humidity and a large number of people. Fungi can persist on surfaces, in fabrics, and on personal items.
Main routes of infection:
- visiting swimming pools, saunas, gyms without individual footwear;
- using someone else’s towels or shoes;
- contact with surfaces in wet public places;
- non-sterile manicure or pedicure tools;
- close household contact with a person who has a fungal infection.
The infection penetrates through microcracks, abrasions, or areas of nail detachment, which often go unnoticed.
Risk factors and conditions that contribute to fungus
Even after contact with the pathogen, the development of the disease largely depends on the condition of the body and the conditions in which the nails are.
Risk factors include:
- increased sweating of the feet;
- wearing tight or poorly ventilated shoes;
- diabetes mellitus;
- circulatory disorders in the lower limbs;
- reduced immunity;
- long-term use of gel polish or traumatic procedures.
A warm and moist environment creates optimal conditions for fungal growth. That is why toenails are affected more often than fingernails. Eliminating provoking factors is an important part of comprehensive treatment and prevention of recurrent infection.
How to treat nail fungus
.jpg)
Treatment of onychomycosis requires a systematic approach, since fungus affects not only the surface of the nail, but also deeper layers of the nail plate and the nail bed. Patients often ask how to remove nail fungus quickly. It is important to remember: there is no universal «quick» method. The nail is restored only as it grows out, so the result is assessed not in a few days, but over weeks and months.
What to use to treat nail fungus: topical remedies
Topical therapy is used when the lesion is limited and the nail plate retains a relatively normal thickness and shape. The main goal is to create a concentration of an antifungal medication in the nail that is sufficient to suppress the pathogen.
Most often used are:
- medicated lacquers with antifungal components;
- creams or solutions to treat the nail fold and the surrounding skin;
- special products to soften and gradually remove the affected layers of the nail.
Topical medications work better if the nail plate is thin or if hygienic treatment has been performed before application and, if necessary, partial filing of the surface layer.
How to get rid of nail fungus: systemic treatment
Systemic therapy — is taking antifungal medications. It is considered when the lesion is pronounced, several nails are involved, the process is long-standing, or topical remedies have not produced results. Such treatment should be prescribed only by a doctor.
Self-treatment with tablets is dangerous and does not increase the chance of success. On the contrary, an incorrect choice of the medication or dosing regimen may lead to lack of effect and adverse reactions.
Who treats nail fungus
Onychomycosis is treated by a dermatologist. During the consultation, the doctor assesses the condition of the nail plates and skin, уточняет длительность изменений, if necessary prescribes a laboratory test and determines the optimal treatment strategy. Further follow-up makes it possible to assess the dynamics of healthy nail regrowth and своевременно adjust therapy if necessary.
How to cure toenail fungus in an advanced form
An advanced form usually requires a combined approach. This means that lacquer or cream alone is often not enough, because a thick affected nail does not allow the medication to penetrate well, and the fungus may persist deep in the nail bed.
Most often in such a situation, the following are combined:
- systemic antifungal medications as prescribed by a doctor;
- topical remedies to support therapy and reduce the risk of spread;
- regular mechanical nail treatment (filing, hygienic pedicure) in a safe режим;
- mandatory treatment of shoes and socks to avoid reinfection.
An important practical point: even with effective treatment, the nail does not «become healthy in a week». Time is needed for a new, unaffected segment to grow out.
How to remove nail fungus
By «removal», patients often mean two different approaches: removal of the affected part of the nail plate or аппаратное/laser intervention as an auxiliary treatment method. The strategy is chosen individually — depending on the thickness of the nail, the area affected, the presence of pain, and the effectiveness of previous therapy.
Possible options:
- step-by-step removal of the affected layers of the nail using special keratolytic products;
- mechanical removal of part of the nail under specialist supervision, if justified;
- laser treatment of fungus as an additional method as part of комплексной therapy, when the doctor considers it appropriate.
Important: nail removal by itself does not guarantee recovery if the infection in the growth zone is not eliminated and antifungal therapy is not carried out.
Prevention of reinfection with nail fungus
Even after successful treatment, a fungal infection can return if the factors that contributed to its development are not eliminated. Fungal spores can persist for a long time in shoes, on socks, towels, and surfaces in the bathroom. That is why prevention is a mandatory part of therapy.
To reduce the risk of reinfection, it is recommended to:
- change socks daily and wash them at a high temperature;
- regularly treat shoes with antifungal sprays or antiseptic agents;
- use only individual towels and manicure tools;
- not walk barefoot in swimming pools, saunas, changing rooms;
- dry the feet thoroughly after washing, especially между toes.
Special attention should be paid to shoes: they should be comfortable, not tight, and хорошо ventilated. постоянная moisture and warmth create an environment in which fungi actively reproduce.
Patients often ask what nail fungus is afraid of. First of all — a dry environment, regular hygiene, adequate treatment, and systematic disinfection of items that contact the feet or hands. It is important not to stop therapy immediately after the внешнего appearance of the nail improves, but to complete the course in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
The information in this article is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as a guide to self-diagnosis or treatment. If symptoms of the disease appear, consult a doctor.
Sources:
PubMed (European guideline for the management of onychomycosis)