bleeding outside the menstrual cycle
Vaginal cancer is most often diagnosed in postmenopausal women. However, it can also develop at a younger age. About 10% of cases occur in patients under the age of 40.
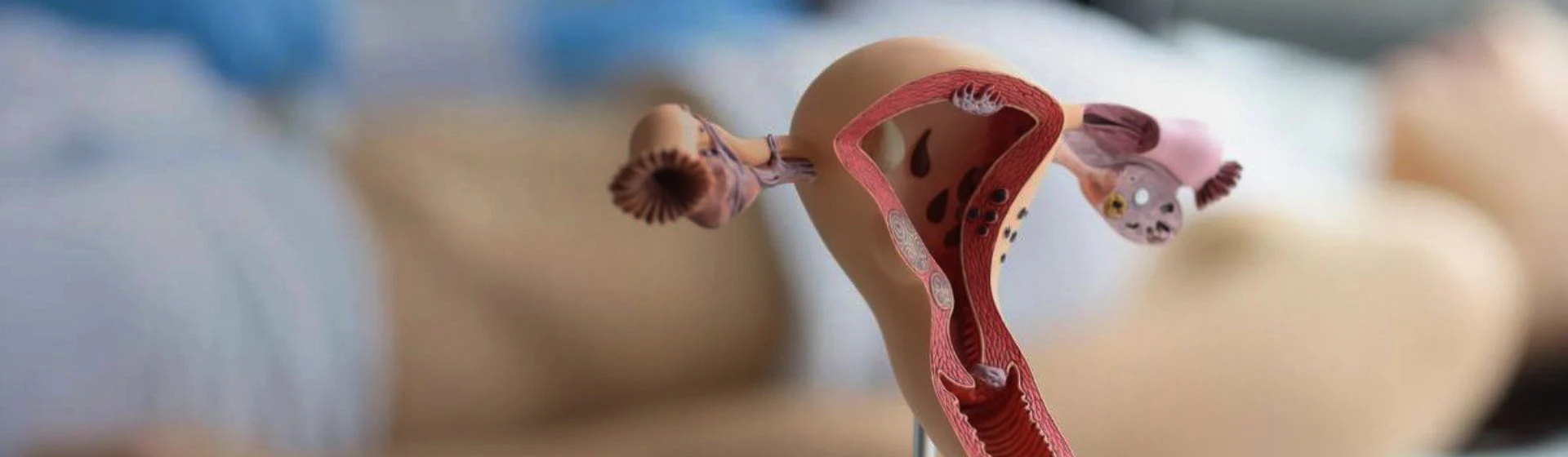
Vaginal cancer is a malignant neoplasm that develops from the cells of the corresponding organ. It accounts for 1 to 3% of oncological diseases of the genitourinary system in women and develops mainly in the postmenopausal period. At a young age, vaginal cancer is very rare and is usually not an independent disease, but a metastasis or secondary lesion caused by cancer of the cervix, uterus, bladder or another organ.

To determine the stage of cancer, oncologists use the international TNM classification system, which involves assessing the size of the tumor, lymph node involvement, and the presence of metastases. Since this system is difficult for patients, a simplified version has been used.
Accordingly, the following stages of vaginal cancer are distinguished:
Symptoms of vaginal cancer may include:
bleeding outside the menstrual cycle
blood in the urine
copious liquid discharge with an unpleasant odor
lower abdominal pain
pain during sexual intercourse
pain when urinating
itching, burning in the genital area
bowel movement disorder
general weakness, weight loss, prolonged fever
The listed symptoms are non-specific. They are characteristic of various gynecological diseases, including inflammatory and infectious, which can be easily cured.
At the initial stage, vaginal cancer can be completely cured - when diagnosed at stage 0 or 1, this happens in more than 90% of cases. But in many women, the disease is detected later due to the lack of symptoms. The tumor can grow for a long time and not cause pain or discomfort. Signs of the disease appear when it increases in size, grows into adjacent organs or metastasizes.
An obstetrician-gynecologist can suspect the presence of a tumor during a visual examination, as well as based on the results of a PAP test. Not only cancer, but also many other diseases can develop secretly, so women are recommended to visit a doctor 1-2 times a year for preventive purposes.
To clarify the diagnosis, a gynecologist may prescribe:
Histological analysis allows you to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of neoplasm. To perform it, a biopsy is performed - under ultrasound control, a thin needle is used to pierce the tumor and a small piece of tissue is pinched off.
Other examinations are performed to determine the extent of the spread of cancer.
The tactics of treating vaginal cancer depend on the size of the tumor, the depth of its growth, the damage to adjacent organs, and the presence of metastases. In most cases, complex therapy is used, which in various combinations and sequences may include:
When diagnosing vaginal cancer at an early stage, as a rule, surgery is performed immediately - only the changed tissues are removed, preserving the organ. A more radical operation may be required if the tumor increases in size and grows into adjacent organs. Depending on the indications, the entire vagina is removed or together with nearby lymph nodes, the uterus, part of the affected bladder, intestines and other organs. In each case, surgeons try to completely remove the tumor, preserving the maximum amount of healthy tissue.
In advanced cancer, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are also used. They can be performed separately or in combination. The advantage of chemotherapy is that it affects the entire body, which is important for the treatment of metastases and the prevention of relapse after surgery.
At Oxford Medical, cancer treatment is carried out by highly qualified oncologists and surgeons with many years of experience. For each patient, they develop an individual treatment program, using state and international therapy protocols, the effectiveness of which has been confirmed by numerous studies.
Oxford Medical is a network of modern medical centers, one of the largest in Ukraine. In Kyiv alone, there are 10 clinics, including a high-tech surgical hospital and an oncology department.
To schedule a consultation, call our contact center or write to the chat on the website.
In most cases, vaginal cancer is a secondary lesion and develops against the background of a malignant process in the cervix, vagina, bladder or breast.
Risk factors for cancer of this location are:
To prevent vaginal cancer, women are recommended to undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist, timely treat all diseases, get vaccinated against oncogenic types of HPV, give up smoking and other bad habits.
Vaginal cancer is most often diagnosed in postmenopausal women. However, it can also develop at a younger age. About 10% of cases occur in patients under the age of 40.
Vaginal cancer is treated by an oncologist or gynecological oncologist.
When treatment is started at an early stage, 90% of women recover completely, at stages 2-3, 5-year survival reaches 50-60%, while at stage 4 the prognosis is less favorable.


