visually noticeable curvature of the spine
The angle of curvature is from 5 to 10%. It may be noticeable in the standing position due to the asymmetry of the shoulders and shoulder blades, but completely disappears when the person lies down.

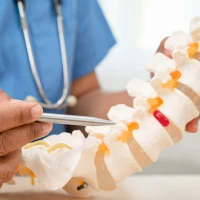
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine, which is accompanied by twisting of the vertebrae along their axis. It can cause chronic back pain, headaches, and dysfunction of internal organs.
True scoliosis is a fairly rare disease and is diagnosed in 2-3% of the population. At the same time, scoliotic posture, on the contrary, is very common - according to statistics, in every 5th schoolchild or office worker.
The difference between scoliotic posture and scoliosis is the absence of structural changes in the tissues of the spine. That is, the curvature appears when a person relaxes his muscles and does not monitor his posture, but with conscious straightening of the back it completely disappears.
Oxford Medical employs experienced specialists and has expert-class equipment. Thanks to this, each patient can undergo accurate diagnostics and treatment of scoliosis or scoliotic posture.
Scoliosis can be caused by abnormalities in the development of the spine or systemic diseases, as well as behavioral habits.
Risk factors include:
Acquired scoliosis most often develops during adolescence, when the skeleton grows rapidly, but the muscle corset remains underdeveloped. Combined with slouching, uneven or excessive loads on the back muscles, and hormonal changes in the body, this significantly increases the risk of spinal curvature.
You should consult an orthopedic traumatologist
if a child or adult has:
visually noticeable curvature of the spine
asymmetrical arrangement of the pelvic bones
location of shoulders and shoulder blades at different heights
asymmetry of the waist and bulging ribs on one side
Secondary symptoms may include frequent headaches, back pain, shortness of breath, and tachycardia.
Scoliosis causes structural changes in the tissues of the spine, which means that the curvature remains regardless of body position. With a scoliotic posture, the spine may be completely straight when a person lies down or stands up and consciously straightens their back. But even in this case, a specialist consultation is necessary—a scoliotic posture also requires treatment.
In the early stages, the signs of scoliosis may not be noticeable from the side. They are often mistaken for ordinary slouching. Only an experienced specialist can detect the disease in a timely manner by conducting an examination and, if necessary, an X-ray or other tests.
There are several types of scoliosis depending on the location and shape of the curvature.
Scoliosis is classified by location:
Depending on the shape of the curvature, scoliosis can be:
In addition, other types of spinal curvature, such as kyphosis and lordosis, are also commonly referred to as scoliosis. However, these conditions do not involve lateral curvature or deformation of the vertebrae. Kyphosis is a backward curvature of the spine (manifested as stooped posture), and lordosis is a forward curvature (manifested as a protruding abdomen).
Scoliosis is also classified according to its causative factor as:
Depending on how pronounced the spinal deformity is, 4 degrees of scoliosis are determined:
The angle of curvature is from 5 to 10%. It may be noticeable in the standing position due to the asymmetry of the shoulders and shoulder blades, but completely disappears when the person lies down.
The angle of curvature is from 11 to 25%. The lateral deformation becomes more noticeable and is not hidden in the supine position. The bottom of the scapula on the curved side of the spine bulges and adheres to the back. There is a skew of the pelvic bones.
The angle of curvature is from 26 to 50%. The spine is strongly curved to one side, resulting in a rib hump and shortening of the trunk. There is also a pelvic tilt and shortening of the leg on the side of the bend.
The angle of curvature is more than 51%. The torso deviates from the vertical axis in the direction of the curvature of the spine. Muscle deformation and dysfunction of internal organs appear.
If you suspect scoliosis, you should consult an orthopedic traumatologist. As part of the diagnosis, the doctor will conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe an X-ray or CT scan.
Spinal curvature can be detected using simple tests: determining the symmetry of the shoulders, shoulder blades, waist curves, and pelvic bones, as well as examining the spine when bending forward.
Hardware studies allow you to clarify the diagnosis and degree of curvature, identify structural abnormalities, and determine the condition of the muscles and ligaments around the spine.

Conservative treatment methods are most often used for scoliosis, but surgical intervention may be necessary for spinal curvature of 3-4 degrees.
Conservative methods include:
Strengthening the back muscles, which hold the spine in a certain position, plays a key role in the treatment of mild forms of scoliosis. Massage, therapeutic exercise, and other techniques are used for this purpose. It is very important that the exercises and level of load are selected individually for each patient. Wearing corrective corsets also provides good results.
It should be noted that the treatment of scoliosis is a long process that requires strict adherence to all medical recommendations. At the same time, the earlier the therapy begins, the more effective it is.
Oxford Medical employs highly qualified orthopedic traumatologists. They have many years of experience in treating scoliosis and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system of varying degrees of complexity. Thanks to this, as well as the availability of expert-class diagnostic and therapeutic equipment in the clinic, each patient receives the necessary medical care.
To make an appointment with an orthopedic traumatologist, call our contact center or leave a request on the website.
Scoliosis – is a serious disease. In addition to an aesthetic defect,
it causes a number of pathological changes throughout the body.
It is recommended to start treatment for scoliosis as early as possible.
This often helps to stop the curvature of the spine and avoid complications.
With significant curvature of the spine, the following may develop:
constant back and chest pain
headaches
muscular dystonia
dysfunction of internal organs
cardiopulmonary failure
To reduce the risk of developing scoliosis and other spinal curvatures, it is recommended to: