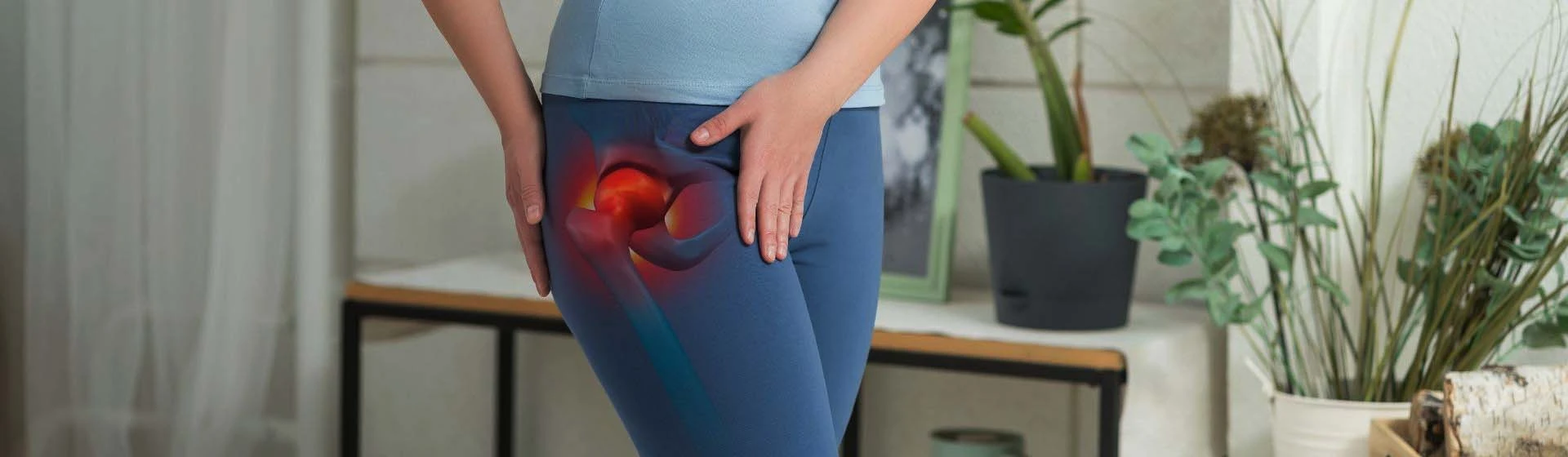
severe pain — sharp or increasing pain in the hip or hip joint area, which intensifies with movement;
Conservative therapy is used mainly for stable fractures without displacement or when surgery is contraindicated. Treatment aims to reduce pain, prevent complications, and create conditions for bone healing.
Main components:
- immobilization of the injured limb (primarily through skeletal traction, which maintains proper alignment of the bone fragments over time; this also includes limiting physical activity and avoiding weight-bearing on the injured leg);
- medication-based pain management and prevention of thromboembolic complications;
- monitoring the patient’s general condition, especially in older adults;
- gradual introduction of therapeutic exercise under medical supervision.