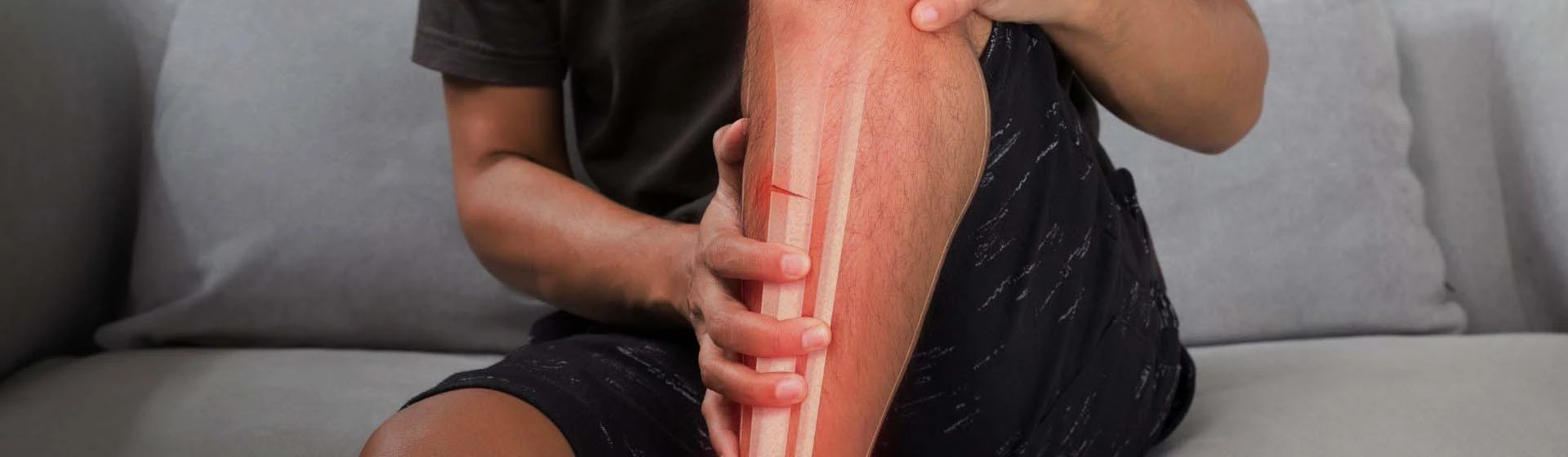
Evaluation of a suspected tibial fracture begins with an examination by an orthopedic traumatologist. The doctor assesses deformity, pain, swelling, bruising, joint mobility impairment, and the ability to bear weight on the leg.
If a tibial fracture is suspected, X-ray imaging is the primary diagnostic method, allowing confirmation of the fracture, determination of its location, and assessment of the injury pattern.
In complex or unclear cases, additional diagnostic methods may be prescribed:
- Computed tomography (CT) – for precise assessment of complex fractures, comminuted injuries, and damage to joint surfaces
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – if ligament or tendon injuries are suspected
This comprehensive approach helps identify complications in a timely manner and choose the optimal treatment strategy, ensuring safe and rapid restoration of leg function.