The information in the article is provided for informational purposes only and is not a guide to self-diagnosis and treatment. If symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor.
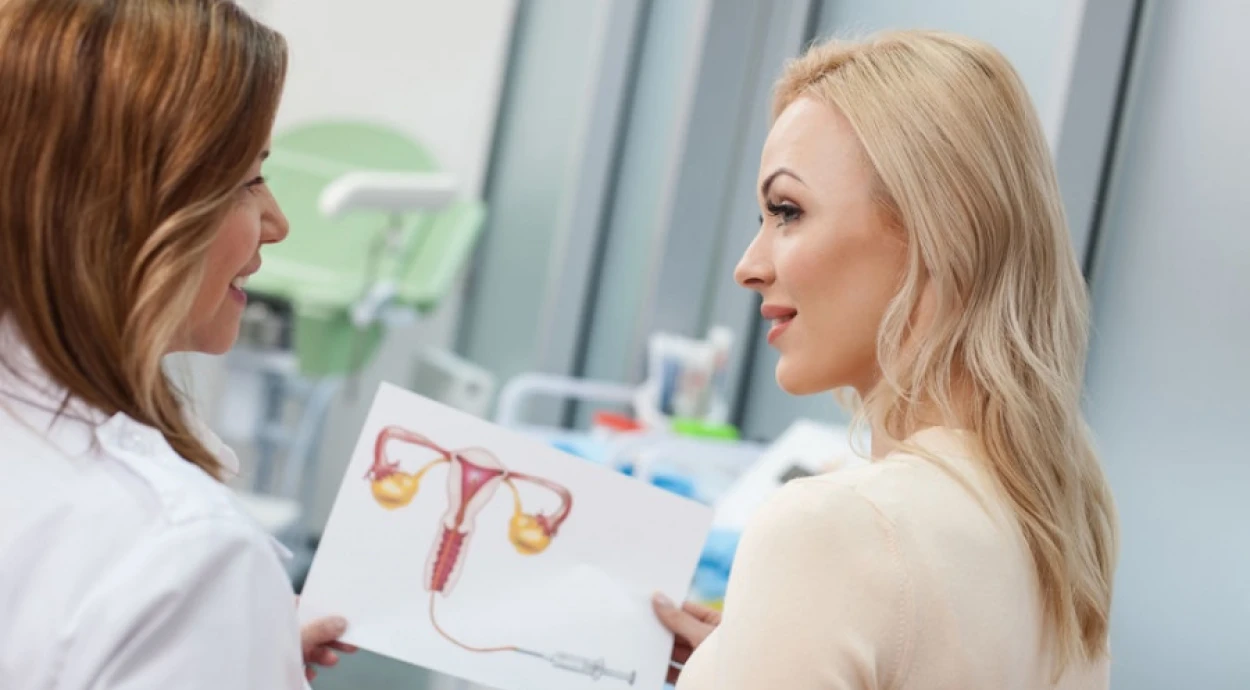
Adenomyosis is the growth of endometrial cells, which make up the uterine mucosa, into the muscle layer.
The condition of the endometrium depends on the level of female sex hormones and changes during the menstrual cycle. Initially, it develops, preparing the uterine mucosa for embryo implantation, and then, if conception does not occur, it is partially rejected and leaves the body during menstruation.
Normally, endometrial cells develop only on the uterine mucosa, but with adenomyosis they penetrate deeper into the muscle layer (myometrium). This is accompanied by pain during menstruation, an increase in its duration and abundance of discharge, as well as uterine bleeding.
The treatment of adenomyosis is carried out mainly by conservative methods, surgical methods are used only in severe forms of the disease. The choice of treatment tactics depends on the degree of the disease, the woman's age and reproductive plans.
Causes of adenomyosis
The causes of the development of adenomyosis are still being studied. Experts have found that the likelihood of the disease is increased by:
-
genetic predisposition;
-
imbalance of female sex hormones;
-
menstrual cycle disorders;
-
chronic infections and inflammation of the reproductive organs;
-
endocrine diseases;
-
abortion;
-
uterine scraping;
-
long-term use of intrauterine contraceptives (IUDs);
-
cesarean section;
-
absence of pregnancy and natural childbirth;
-
weak immunity and other factors.
Some experts also note that adenomyosis is more common in women who often experience stress and perform excessive physical exertion.

Symptoms of adenomyosis
The main symptoms of adenomyosis are pain before and during menstruation, as well as an increase in the volume of blood discharge.
Symptoms of adenomyosis include:
-
increased duration of menstruation;
-
increased volume of menstrual discharge;
-
discharge of a large number of clots;
-
small discharge a few days before and after menstruation;
-
bleeding discharge in the middle of the cycle;
-
sharp, throbbing pain before menstruation and during the first days;
-
increased size of the uterus.
In the early stages, adenomyosis may develop asymptomatically. Signs of the disease usually appear with deep endometrial growth or the development of nodes and adhesions.
Forms and stages of adenomyosis
Depending on how the endometrium grows into the muscle layer, 4 forms of the disease are distinguished:
-
diffuse - the endometrium grows evenly throughout the muscle layer of the uterus;
-
focal - the endometrium grows into the myometrium only in some places;
-
nodular - in places of active endometrial growth, nodes similar to fibroids are formed;
-
diffuse-nodular - The endometrium spreads throughout the muscle layer, but in some places it grows more strongly and provokes the appearance of nodes.
There are also stages of the disease, which depend on the depth of endometrial growth.
Adenomyosis can be:
-
Stage 1 - the endometrium grows only into the submucosal layer;
-
Stage 2 - the endometrium penetrates the muscle layer by less than 50% of its thickness;
-
Stage 3 - the disease affects more than 50% of the thickness of the myometrium;
-
Stage 4 - endometrium grows through the myometrium and can spread to neighboring organs (endometriosis).
Diagnosis of adenomyosis
The symptoms of adenomyosis are non-specific. Other diseases can manifest themselves in a similar way. A comprehensive diagnosis is required to make a diagnosis.
During the consultation, the gynecologist studies the patient's symptoms and medical history. The doctor also conducts a chairside examination, which allows you to determine the size of the uterus. Adenomyosis is characterized by its enlargement and the formation of nodular seals on the walls.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the gynecologist may prescribe:
-
blood, urine and urogenital tests discharge;
-
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
-
Computed tomography (CT);
-
Hysteroscopy - endoscopic examination of the uterus;
-
Tissue biopsy and histological analysis.
In some cases, it is difficult to determine whether uterine changes are the result of adenomyosis, fibroids or malignant neoplasms. Therefore, hysteroscopy and other studies may be performed for differential diagnosis.
Treatment of adenomyosis at «Oxford Medical»
Treatment of adenomyosis is carried out using conservative therapy. Surgical treatment is resorted to in some cases in severe forms of the disease.
The doctor determines the treatment tactics individually depending on the form and stage of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies, the woman's age and other factors.
Drug therapy, as a rule, involves the appointment of painkillers to improve well-being before and during menstruation, iron-containing drugs to eliminate anemia, as well as hormonal agents. These can be progestogens, which stimulate the development of normal endometrium and prevent its hyperplasia, or androgens, which block the action of female sex hormones and cause thinning of the endometrium, or other drugs.
Surgical treatment is prescribed mainly in severe forms of adenomyosis and the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment.
In «Oxford Medical» In case of gynecological pathologies, operations are performed using the hysteroscopic or laparoscopic method in a 24-hour surgical hospital with two modern operating rooms and comfortable postoperative wards.
At «Oxford Medical» surgeons work according to the Fast Track Surgery rapid rehabilitation protocol. It allows:
-
to facilitate preoperative preparation (no bowel cleansing required);
-
to reduce pain after surgery (with laparoscopy, the puncture sites are anesthetized);
-
not to use a urinary catheter and drainage tubes during surgery;
-
to get out of bed almost immediately after surgery (when working according to the classic protocol, bed rest is mandatory without visiting the toilet for 1 day);
-
to turn freely in bed (no need to lie only on your back for a day);
-
not to restrict nutrition after surgery;
-
not to bandage or remove sutures;
-
return to your usual lifestyle in 1-2 days.
Prevention of adenomyosis
To prevent the development of adenomyosis, it is recommended to:
-
have annual preventive examinations;
-
treat all gynecological diseases in a timely manner;
-
treat and prevent endocrine diseases;
-
monitor your hormonal background;
-
take hormonal drugs only as prescribed by a doctor;
-
do not have abortions;
-
implement reproductive function;
-
lead a healthy lifestyle.
Make an appointment for a consultation or learn more about the diagnosis and treatment of adenomyosis at «Oxford Medical» you can by calling our contact center or writing in the chat.
Sources: