Сontents
- Who is prone to weather sensitivity?
- Causes of weather sensitivity
- Symptoms of weather sensitivity
- Types and degrees of weather sensitivity
- Weather sensitivity in vegetovascular dystonia
- Why does discomfort appear in joints and body parts where injuries occurred when the weather changes?
- Which doctors treat weather sensitivity?
- Treatment and prevention of weather sensitivity
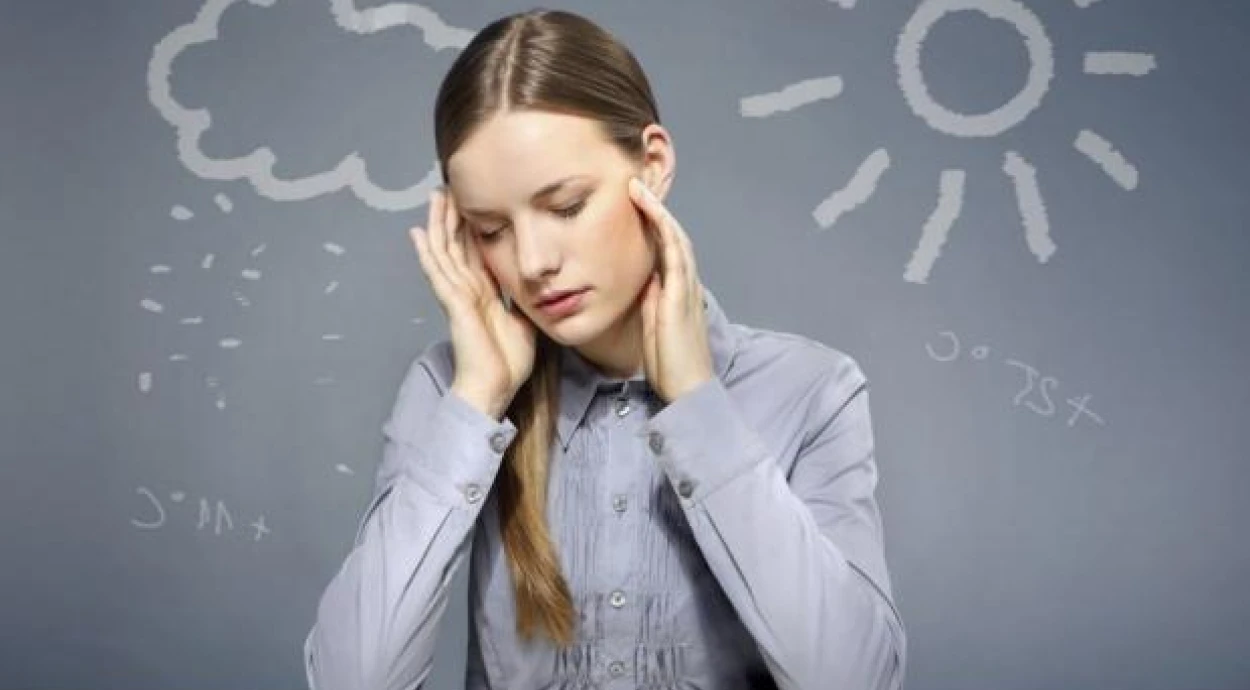
Weather sensitivity is the body’s sensitivity to changes in weather conditions: sudden cooling or warming, fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, magnetic storms, or even solar flares. It can manifest as headaches, weakness, loss of appetite, heart rhythm disturbances, and other symptoms. Most often, the malaise lasts from 1 to 4 days.
Who is prone to weather sensitivity?
In the USA, a study was conducted to determine how many people suffer from weather sensitivity. The results showed that every third person experiences malaise, but the symptoms and severity vary significantly among individuals. It turned out that residents of rural regions almost do not feel the effects of weather changes, while people living in large cities tolerate them quite poorly. This is associated with a narrowing of the microclimatic comfort zone, which occurs with a sedentary lifestyle, the predominance of intellectual work over physical activity, and rare walks in the fresh air.
Causes of weather sensitivity
Many people do not notice this, but their well-being is affected by a whole range of factors. In addition to nutrition, physical activity, and healthy or harmful habits, the environment plays a significant role. Changes in air temperature and atmospheric pressure, cloudy or sunny weather — all this affects health and emotional state. Some people adapt more easily and quickly, which is why they do not even pay attention to the changes, while others do not.
Causes of increased weather sensitivity are considered to be:
-
decreased immunity and general weakness;
-
hypo- and hypertension;
-
cardiovascular diseases;
-
bronchial asthma;
-
rheumatism;
-
arthritis;
-
atherosclerosis;
-
vegetovascular dystonia and other chronic diseases;
-
past concussion or fractures;
-
emotional lability;
-
decreased or increased activity of the nervous system (melancholic and choleric types);
-
old age;
-
insufficient physical activity.
Symptoms of weather sensitivity
Symptoms of weather sensitivity can be purely individual. They depend on the presence of chronic diseases in the patient, their age, lifestyle, emotional state, and other factors.
Most often, patients complain of:
-
weakness, rapid fatigue;
-
loss of appetite;
-
pain in muscles and joints, as well as in places of past fractures;
-
dizziness;
-
headache, migraine;
-
increase or decrease in blood pressure;
-
ringing in the ears;
-
rapid heartbeat;
-
shortness of breath;
-
mood swings, anxiety, irritability, depression.
Specialists note that during sudden weather changes, as well as magnetic storms and solar flares, the number of calls to emergency medical services increases, cases of exacerbation of chronic diseases rise, as well as the number of road accidents and other incidents.
Types and degrees of weather sensitivity
Depending on the predominant symptoms, several types of weather sensitivity are distinguished:
-
cerebral — manifests as headaches, migraines, dizziness;
-
cardiac — chest pain, shortness of breath occur;
-
asthenoneurotic — accompanied by insomnia, irritability, blood pressure fluctuations;
-
mixed — combines symptoms of different types.
Also, depending on the severity of symptoms, different degrees of weather sensitivity are distinguished:
-
mild — slight malaise appears, but no physical changes (diagnostically, the person remains completely healthy);
-
moderate — physical changes occur, for example, changes in blood pressure or cardiogram data;
-
severe — dysfunction of the nervous, cardiovascular, or other body systems occurs, chronic diseases worsen.
Weather sensitivity in vegetovascular dystonia
Vegetovascular dystonia (VVD) is a functional disorder of the nervous system that causes disturbances in the functioning of various organs. It may manifest as a complex of different and often interrelated symptoms. The most common are fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, insomnia, emotional lability, and others.
These same symptoms are characteristic of weather sensitivity, which is why people with VVD suffer from it to a greater extent and need medical consultation and therapy selection.
Why does discomfort appear in joints and body parts where injuries occurred when the weather changes?
Scientists from the University of Massachusetts conducted a study and found that 75% of people with arthritis believe that their condition and level of pain depend on weather conditions. Other participants also noted that under changing environmental conditions (cold, rain, etc.) the intensity of pain increases by 20%.
Scientists found a logical explanation for this fact. The thing is that when the weather changes, fluctuations in atmospheric pressure often occur. This, in turn, affects the pressure inside the joint cavities, which can irritate nerve endings and cause pain. Joints and bone tissues in areas of injuries and fractures suffer the most, because their tissues have already been damaged and are more sensitive.
Which doctors treat weather sensitivity?
When symptoms of weather sensitivity appear, it is recommended to consult a family doctor. During the consultation, they will listen to complaints and study the medical history to create the most complete clinical picture.
The symptoms that occur with weather sensitivity can be caused by various diseases. Therefore, first of all, health problems must be ruled out. For this, the doctor may prescribe tests and instrumental diagnostics (ultrasound, ECG, and others).
If disorders are detected, the family doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment or refer to a specialist.
If it is confirmed that the symptoms are a consequence of increased weather sensitivity, the doctor will advise how to alleviate the condition.
Treatment and prevention of weather sensitivity
In the presence of chronic diseases, if they worsen during changes in weather conditions, it is necessary to consult your doctor and receive individual recommendations. If necessary, the specialist may prescribe medication therapy.
In other cases, if a person does not have serious health problems, to reduce weather sensitivity it is recommended to:
-
give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol consumption);
-
establish a balanced diet that includes all essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals;
-
exercise regularly;
-
walk more in the fresh air;
-
sleep 8 hours a day (at least during days of weather anomalies);
-
avoid stressful situations;
-
control your emotional state;
-
practice breathing exercises;
-
drink herbal tea, etc.
Doctors note a strong connection of weather sensitivity not only with a person’s age and health but also with their psycho-emotional state. Therefore, it is important to control the level of stress and anxiety, and if necessary, consult a psychotherapist or another specialist.