Contents:
-
What are the possible consequences of self-medication without consulting a specialist?
-
How to properly assess symptoms and determine which doctor to see?
-
Why is it important to follow prescribed dosages and courses of treatment?
-
How does self-medication affect the effectiveness of medications and the development of antibiotic resistance?
-
What factors should be considered before deciding to resort to self-medication?
-
Frequently Asked Questions
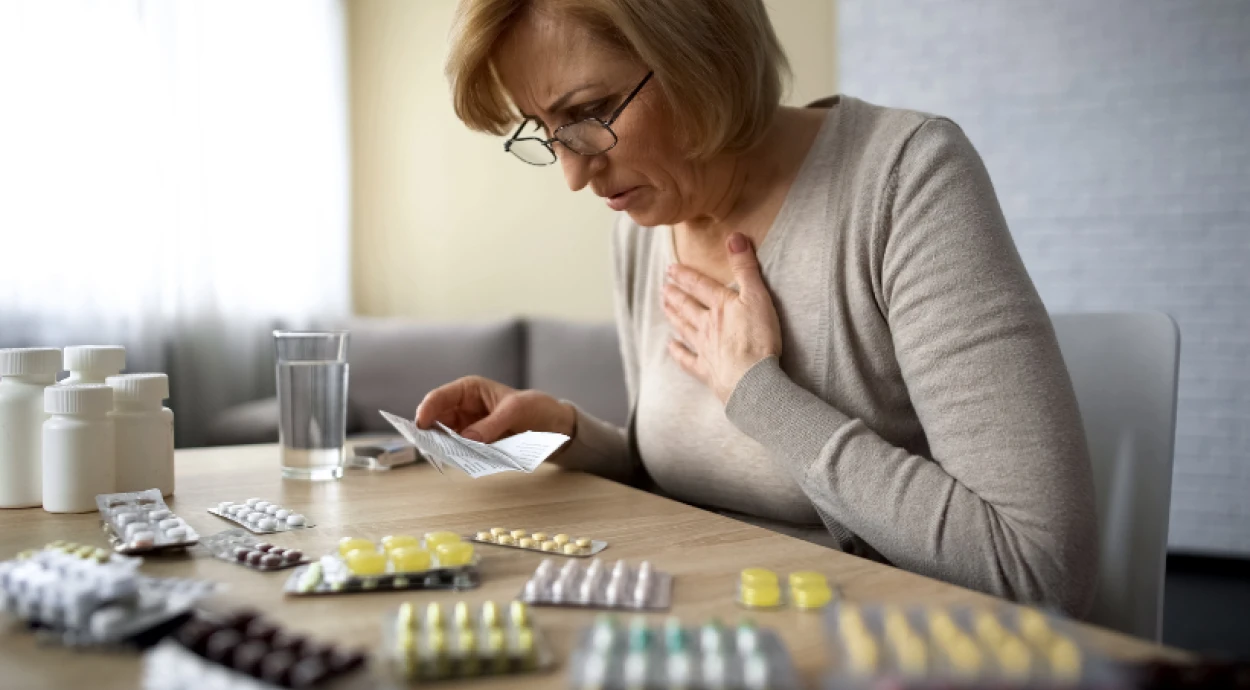
“Self-medication can be harmful to your health” – this statement accompanies almost all information about diagnostic and treatment methods, as well as medicines. It is so widespread that many no longer perceive it with due seriousness.
Sometimes it seems that the illness is not serious, there is no time to see a doctor, and the problem can be solved independently. Symptoms can be “googled” or advice can be sought from a pharmacist at a pharmacy. However, it is not that simple. After all, doctors study for at least six years for a reason.
The human body is a very complex system in which everything is interconnected. Different diseases can cause similar symptoms. A correct diagnosis can only be made based on the results of an examination. As for treatment, it must be individually selected by a doctor. Otherwise, it is very easy to allow the further progression of the disease and the development of complications.
In this article, we will examine why self-medication is not the best option and what dangers it entails.
What are the possible consequences of self-medication without consulting a specialist?
The main risks of self-medication are:
-
incorrect diagnosis and taking medications that are ineffective in this case;
-
improvement of symptoms under the influence of drugs without full recovery;
-
transition of the disease into a chronic stage;
-
progression of the disease and development of complications due to inappropriate treatment;
-
loss of time – the effectiveness of treatment for some diseases depends on timely diagnosis and the start of proper therapy;
-
development of side effects from taking medications.
Self-medication is especially dangerous if symptoms of diseases of the cardiovascular, nervous, genitourinary or respiratory systems, digestive tract and intestines, joints and spine, as well as hormonal disorders occur.
Specialists at Oxford Medical warn that self-medication is contraindicated for children, pregnant women, the elderly, and patients with chronic diseases who take certain medications for a long time. In such cases, there is a high risk of incorrect use of drugs due to ignorance of all contraindications and their interactions with other medicines.
How to properly assess symptoms and determine which doctor to see?
The Ministry of Health of Ukraine recommends that in case of illness, you should first contact a family doctor or therapist. This is a general practitioner who has knowledge in many areas of medicine. Their task is to carry out initial diagnostics and treatment of many acute and chronic diseases, and in complex cases – to refer the patient to a narrow specialist.
This approach allows you to immediately receive qualified help and not waste time searching for the right specialist yourself. If the illness is beyond the doctor’s qualifications, they will simply refer the patient to another specialist.
However, sometimes symptoms can almost precisely indicate which organ or system is affected. In such cases, you can immediately see the appropriate doctor.
Consultation with a cardiologist is recommended in case of:
-
pain in the heart area;
-
shortness of breath during light physical exertion or at rest;
-
sensations of “pauses” in heartbeats;
-
low or high pulse;
-
changes in blood pressure.
You should see a neurologist if you are experiencing:
-
headache;
-
dizziness;
-
numbness in hands or feet, tremor, sensory disturbances;
-
weakness in the legs, unsteady gait;
-
seizures;
-
ringing in the ears, flashing spots before the eyes;
-
memory impairment, insomnia, etc.
An otolaryngologist (ENT) consultation is necessary in case of:
-
hearing impairment;
-
hoarseness of voice;
-
prolonged runny nose, nasal congestion;
-
snoring;
-
sore throat and other symptoms of ear, throat, or nose diseases.
A gastroenterologist consultation is recommended if you experience:
-
pain in the side or abdomen;
-
heartburn, belching, hiccups;
-
bitterness in the mouth, nausea, and vomiting;
-
bowel movement disorders.
In case of rashes or other skin problems, you can see a dermatologist. Joint and spine diseases are treated by an orthopedic-traumatologist, and vascular diseases – by a phlebologist.
If urination disorders occur, you need a urologist’s consultation. For complaints related to the genitourinary system, women are recommended to see a gynecologist, and men – a urologist-andrologist.
Why is it important to follow prescribed dosages and courses of treatment?
Any medications should be taken as prescribed by a doctor. It is equally important to adhere to the prescribed dosages and duration of treatment.
It is not advisable to stop taking medications early, since relief of symptoms is not a guarantee of full recovery. Interrupting treatment can lead to worsening of the disease or its transition into a chronic stage.
If, on the contrary, the medication does not improve well-being, taking it longer than prescribed makes no sense. It may be ineffective in this case, and another treatment is needed. To do this, you should consult your doctor again.
Also, you should not refuse one or more prescribed medications. The doctor may recommend several drugs to ensure comprehensive treatment.
How does self-medication affect the effectiveness of medications and the development of antibiotic resistance?
One of the problems of self-medication is the development of antibiotic resistance – the resistance of different bacterial strains to antibacterial drugs. As a result, they become ineffective in relevant bacterial diseases, which greatly complicates treatment and leads to disease progression.
Antibiotics should only be taken when indicated – specifically in cases of bacterial disease. They do not work for viral, fungal, or parasitic infections.
Also, in case of uncontrolled or prolonged use of other medications, the body may develop dependence on them and their effectiveness may decrease.
What factors should be considered before deciding to resort to self-medication?
Self-medication is acceptable only in case of mild cold symptoms and improvement of well-being within a few days. In all other cases, you must consult a doctor for diagnostics and appropriate treatment.
It should be taken into account that self-administration of medications carries a high risk of complications.
At Oxford Medical, you can receive a consultation not only at one of the clinics located in different districts of Kyiv, but also online.
Frequently Asked Questions
What risks are associated with improper use of medications?
With improper use of medications, side effects and complications may develop in both the affected and healthy organ or system. In addition, there is a risk of worsening symptoms against the background of the disease transitioning into a latent form or chronic course.
How does self-medication affect long-term health and treatment effectiveness?
As a result of self-medication, there is a risk of missing the onset of a serious disease. This may lead to complications and the need for more complex treatment. The disease may also progress to a chronic stage.
In addition, in case of incorrect or frequent use of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance develops. This reduces the effectiveness of drugs for bacterial diseases.
Sources:
-
National Library of Medicine https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20615179/
-
ResearchGate https://www.researchgate.net/publication/45112723_Risks_of_Self-Medication_Practices
-
MDPI journals https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/56/6/312
-
Oxford University Press https://academic.oup.com/occmed/article/61/7/490/1462971