gastritis
EGD (fibro-esophago-gastro-duodenoscopy) is a modern, informative and safe method of examining the upper gastrointestinal tract using a special endoscope. The method is used to detect gastritis, ulcers, tumors, and bleeding.

A gastroscopy is the examination of organs of gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum) by the gastroscope, a special instrument, which is inserted in the patient’s mouth.
The gastroscopy is an absolutely safe procedure; the only contraindication is the presence of severe burns of the esophagus. The stomachache is not the contraindication, but, on the contrary, it is the reason for vising the gastroenterologist.
Gastroscopy is an examination of the organs of the scutulo-intestinal tract (the duct, the scutum, the duodenum) with the help of a gastroscope - a special instrument that is inserted through the mouth of the patient.
Gastroscopy is an absolutely safe procedure, the only contraindication is the presence of acute pain in the patient. Pain in the vulva is not a contraindication, but rather, as a matter of fact, it’s time to contact a gastroenterologist.
The gastroscopy allows examining the condition of upper sections of the gastrointestinal tract
in maximum detail.
It is required in case of:
gastritis
duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum)
esophagitis (inflammation of esophageal mucosa)
ulcer of the stomach or duodenum
suspicion of tumor or bleeding of said organs
The preparation is not difficult: you need to come fasting (not eat for minimum 8-10 hours) and warn the doctor about presence of diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus) and allergy to medications. Upon request, the patient may be given a local anesthesia of throat by using a spray with anesthetic.
While undergoing the gastroscopy, you may feel unpleasant feelings, but now it is the most reliable method of obtaining precise and comprehensive data on the condition of the esophagus, stomach or duodenum. The use of premedication and painkilling drugs in combination with modern equipment allows reducing these feelings to minimum.
The performance of gastroscopy by using medication sleep allows undergoing the procedure without any unpleasant feelings.
You can obtain additional information and make appointment for gastroscopy in Oxford Medical Kyiv clinic by calling us.
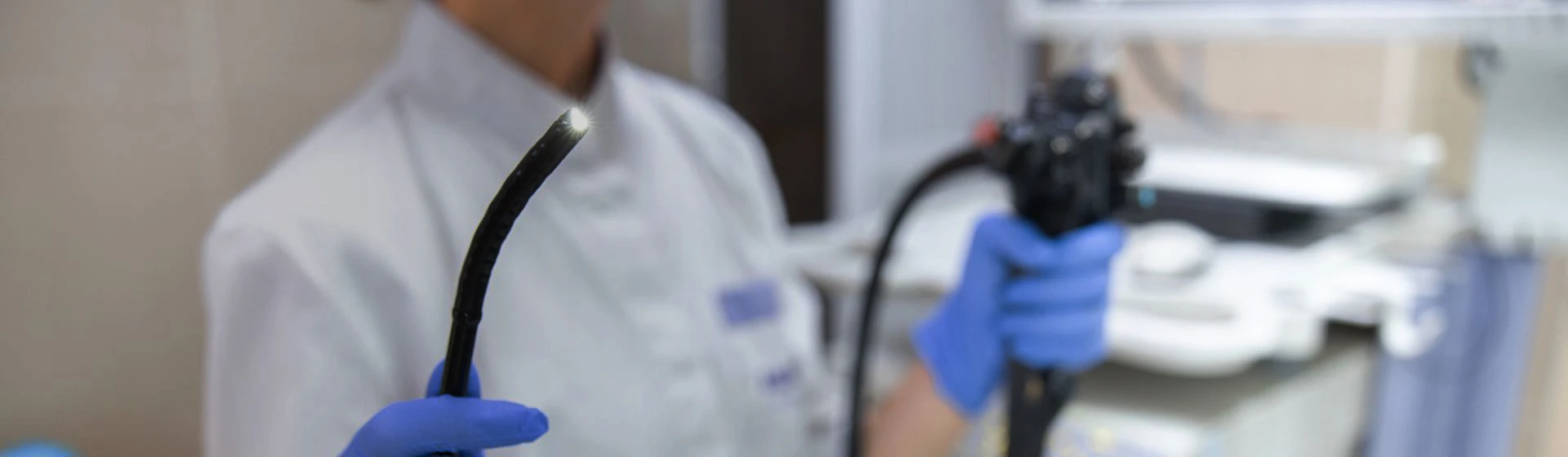
Only the experienced endoscopist performs the diagnosis. The gastroscope is a thin, long and flexible fiber-optic tube, at the tip of which there is a camera. Lying on his side, the patient clenches with teeth a special mouthpiece, through which the gastroscope tube is inserted into the mouth, and then in the esophagus. The doctor carefully examines the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, recording the image, where it is necessary. The gastroscope allows getting a biopsy, removing small polyps, performing other medical manipulations.
On the average, the gastroscopy procedure takes not more than two-three minutes. If necessary, the gastroscopy record can be viewed by the doctor at any moment. The complications after the gastroscopy are rare and virtually absent if the gastroscopy was performed by the qualified and experienced doctors.
The gastroscopy allows detecting and immediately removing the gastric polyps – benign tumors, which over time can degenerate into cancerous tumors.
The cost of gastroscopy with local anesthesia includes:
The cost of sleep gastroscopy includes:
The effectiveness of gastroscopy may vary. At the Oxford Medical clinic Various packages of services are available so that each patient can choose the best option for his or her condition. Standard gastroduodenoscopy is suitable for basic diagnosis and allows for a clear examination of the duct, scutum and duodenum. To increase comfort, it is possible to perform gastroduodenoscopy with local anesthesia, since this procedure is practically painless. If maximum comfort is required or anxiety is increased, gastroduodenoscopy can be reversed with internal anesthesia — This option transfers the procedure to the medicinal sleep station.
A locally available package that includes a one-hour gastroscopy and colonoscopy under internal anesthesia. This is useful for patients who need to carry out a comprehensive diagnosis of colon in one day.
The choice between packages depends on the clinical situation, individual characteristics of the patient and the doctor’s recommendation. You can find out more information about the price of gastroscopy in skin lesions here.
At Oxford Medical FGDS can be completed as comfortably as possible, even if it is carried out unfastened under either local or general anesthesia.
There are two types of anesthesia for gastroscopy: local or sedation. With local anesthesia, a spray anesthetic is applied to the patient's throat, which reduces sensitivity and reduces discomfort during the procedure. A sedated patient, on the other hand, is asleep and experiences no discomfort.
The examination of a sedated patient differs slightly from a standard procedure. First, the anesthesiologist induces a sedative-induced state with special medications, after which an endoscopist performs the examination. The patient is transported to a day hospital ward, where they remain until the effects of the sedative-induced state wear off.
Sedation gastroscopy allows for the same range of examinations as a standard gastroscopy: examination, image recording, tissue sampling (biopsy) for examination, and removal of some polyps.
EGD (fibro-esophago-gastro-duodenoscopy) is a modern, informative and safe method of examining the upper gastrointestinal tract using a special endoscope. The method is used to detect gastritis, ulcers, tumors, and bleeding.
Gastroduodenoscopy is a procedure that allows you to examine the inner surface of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. It is performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes: taking a biopsy, removing polyps in the stomach, stopping bleeding.
Preparation for gastroduodenoscopy includes abstaining from food for at least 8–10 hours before the procedure. It is important to inform the doctor about any existing diseases, medications, and allergies. If necessary, local anesthesia or sedation is used to increase comfort.
Before fibrogastroduodenoscopy, you should not eat or drink for 8–10 hours, and inform the doctor about any chronic diseases, diabetes, or allergies. If a biopsy or premedication is planned, these nuances are further clarified during the consultation.
Preparation for gastroscopy is standard: do not eat or drink for 8–10 hours, and not even water for 2–3 hours. Be sure to inform your doctor about any medications you are taking, your general health, and any allergies.
Gastroendoscopy is an examination of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum using a flexible endoscope equipped with a camera. The procedure allows for the diagnosis of chronic and acute diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Before gastroscopy, it is advisable not to drink water 2–3 hours before the examination, as even a small amount of fluid can affect the accuracy of the diagnosis and provoke nausea during the procedure.
The duration of the procedure depends on the specific clinical situation and the scope of diagnostic or therapeutic manipulations. In most cases, FGDS takes up to 10 minutes. If during the examination there is a need to take a biopsy, remove polyps or perform additional interventions, the procedure may last a little longer.
Before inserting the probe, the doctor will treat your throat with an anesthetic. When the endoscope touches your throat, you should take a sip, relax, and not tense up. Deep breathing through your nose will help reduce discomfort.
You must abstain from eating for 8–10 hours before the procedure. Dinner should be light and no later than 12 hours before the examination. On the morning of the procedure, no food or drinks, not even water.
Do not eat for at least 8–10 hours before gastroscopy. If the examination is scheduled for the morning, the last meal can be eaten the evening before, and then a complete fast can be observed.
The procedure of swallowing a tube is called an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS). It may also be called an esophagogastroduodenoscopy, gastroscopy, or gastroduodenoscopy.
FGDS usually lasts up to 10 minutes. The time depends on the complexity of the clinical situation and the need for additional procedures, such as taking a biopsy or removing polyps.
The patient lies on his side, clamps the mouthguard with his teeth, after which a flexible endoscope is inserted through the mouth. During gastroscopy, the doctor carefully examines the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, assesses the presence of inflammation, ulcers, polyps or other pathological changes, and if necessary, performs additional diagnostic or therapeutic manipulations, for example, takes a biopsy.
Before gastroscopy, you should not eat, drink (2–3 hours before the examination), smoke, take certain medications (especially those that affect blood clotting), or chew gum. The doctor will provide detailed recommendations before the procedure.
To make an appointment for FGDS at the Oxford Medical clinic, simply call our contact center or use the online form on the website. Our specialist will help you choose a convenient time.
EGD is an esophagogastroduodenoscopy, a modern endoscopic method of diagnosing the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The procedure makes it possible to detect inflammation, ulcers, polyps, tumors, sources of bleeding, and also to perform therapeutic manipulations.