pain in the chest
Breast cysts can cause discomfort or pain. However, small cysts are often painless and are only discovered during a routine check-up. If you experience pain or other changes in your breasts, you should see your doctor immediately.
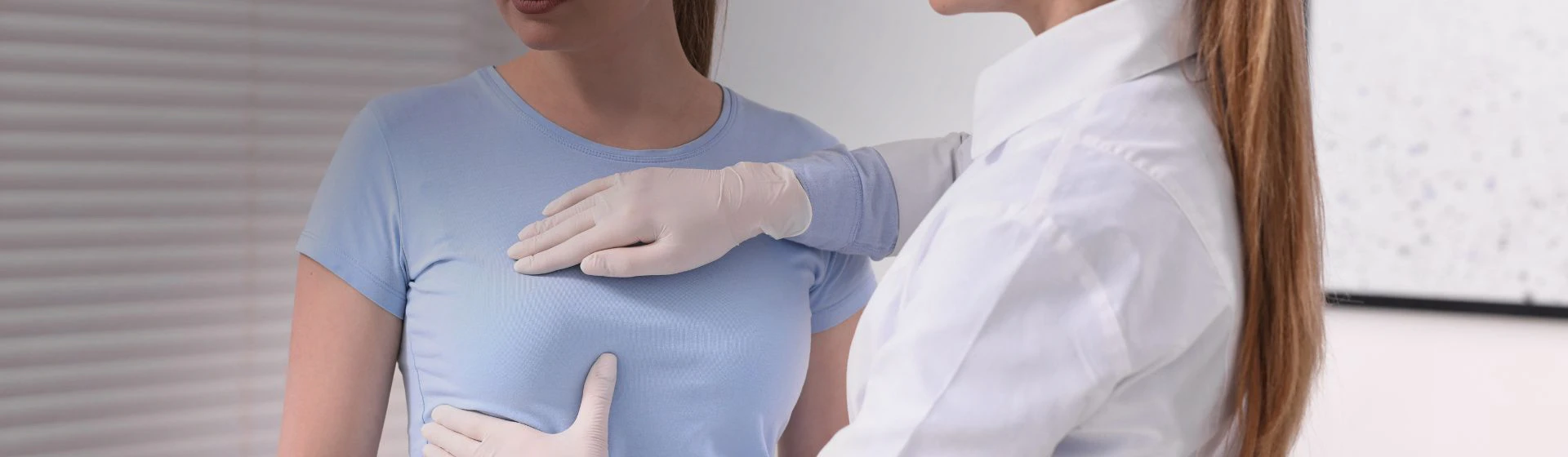
A breast cyst is a capsule filled with fluid that is found in the soft tissues of the breast. Cysts can be single or multiple formations of different sizes (from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter).
The appearance of cysts in the breast can be provoked by gynecological diseases, incorrect intake of hormonal drugs and diseases of the endocrine system.
An important role in breast diseases, including cysts, plays an increased level of prolactin and estrogen, which is often observed in ovarian diseases or inflammatory processes in them. Under the influence of these factors, an increase in the size of one or more ducts of the breast, the accumulation of secretions in them due to the clogging, and the formation of a cyst becomes possible. Blockage of the duct, among other things, can be triggered by papilloma growing inside it.

The severity of symptoms of the cyst is in proportion to its size – the larger the cyst is, the more discomfort it delivers to the patient. Small cysts do not bother a woman, but almost always are detected during preventive examination. Large cysts can cause dragging sensations, pain and a burning sensation.
If the cyst is very large the shape of the breast changes, and the skin acquires a bluish color.
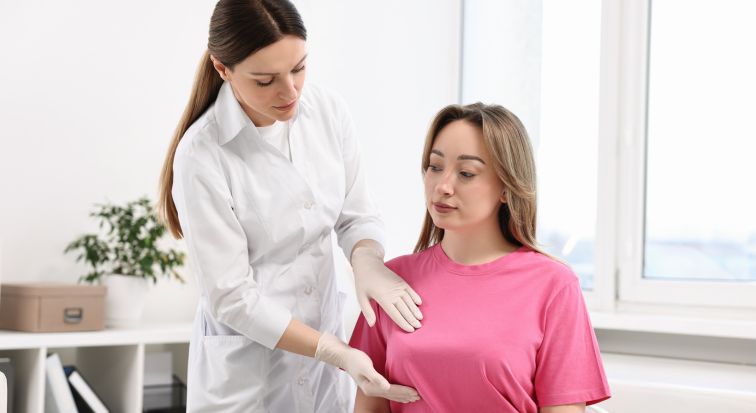
A woman can recognize the cyst by herself during preventive self-examination and palpation of the breast. The cyst is felt as painful when pressed, a stationary seal with clearly defined boundaries.
If the cyst becomes inflamed, the following symptoms may occur:
pain in the chest
dragging sensation, burning
skin redness
enlargement of axillary lymph nodes
temperature rise
Despite the fact that some cysts may not cause discomfort, they need to be examined, because the sides of the cyst, as well as its inner material, can be of a malignant nature. But in the vast majority of cases cysts are benign formations.
As previously noted, a woman can suspect a cyst during an independent examination, palpation also allows the breast physician to assume the presence of a cyst during the initial examination and appoint an additional study -ultrasound of the mammary glands.
Ultrasound allows to confirm not only the fact of proliferation of cysts in the mammary glands, but also to distinguish the cyst from fibroadenoma. These tumors are distinguished by the doctor during palpation (the cyst is stationary, and the fibroadenoma is usually a mobile seal), but the final conclusion is possible only with the results of ultrasound of the mammary glands.
If the size of the cyst is more than one and a half centimeters or its appearance is provoked by the growth of papilloma inside the duct of the breast - a biopsy is prescribed. The procedure means taking a particle of a cyst to conduct a study that excludes its malignant nature. The sample is taken under the control of the ultrasound machine.
Methods of treatment depend on the location of cysts, their number, size and dynamics of development. The way of treatment and its necessity on the whole, the doctor determines after examination and research.
Small (not detected by palpation, visible only on ultrasound) single and non-developing breast cysts should be only controlled during planned visits to the clinic, conservative treatment is also possible. The course usually includes drugs that relieve inflammation, have an absorbable effect and correct the level of hormones. For larger cysts a puncture to pump out the fluid from the cyst or surgery may be indicated.
The cost of treatment depends on the chosen method and the complexity of the case. For example, the price may vary depending on whether a breast cyst puncture will be performed or surgery is prescribed. You can pre-read the prices here. The doctor will inform you in more detail about the program and cost of treatment during the initial consultation.
Make an appointment at a time convenient for you by phone or via online chat on the clinic's website!
Breast cysts can cause discomfort or pain. However, small cysts are often painless and are only discovered during a routine check-up. If you experience pain or other changes in your breasts, you should see your doctor immediately.
A breast cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the breast tissue. It can be single or multiple and can be caused by hormonal changes, trauma, or other factors. Most cysts are benign, but they should be examined to rule out any risks.
Treatment for a breast cyst depends on its size, the presence of symptoms, and other individual factors. The most common procedure is a puncture, which involves removing fluid with a needle under ultrasound guidance. Anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed for inflammation. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Before removing a cyst, a thorough examination is necessary, including an ultrasound or mammogram. If the cyst is causing discomfort, the doctor may order a puncture to remove the fluid. If the cyst refills or develops complications such as inflammation, other methods, including surgical treatment, may be used.
Treatment of a breast cyst may include puncture, drug therapy to relieve inflammation, or surgery in difficult cases. The method is selected individually, taking into account the patient's condition. A timely visit to a mammologist guarantees effective treatment and reduces the risk of complications.