dull or aching pain in the chest
It is used for minor changes. It includes correction of hormonal balance, taking anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins.
Mastopathy is the most common mammological problem that women have to face in their life. It is not an independent disease. Patients with suspected mastopathy are usually women in the age range from 30 to 50 years. Mastopathy is the growth of breast tissue, accompanied by the appearance of seals in the breast, which occur under the influence of endocrine or gynecological problems.

The causes provoking the development of the disease are not reliably ascertained, but the relationship between the appearance of the disease and dysfunction of the endocrine system responsible for the endocrine profile of the body is established. The hormone prolactin, which is actively produced during breastfeeding, can continue to be released after the end of the lactation period, provoking the development of hyperprolactinemia – the main cause of mastopathy (increased prolactin levels are observed in 80-85% of women with mastopathy).
Gynecological diseases can also contribute to the development of mastopathy: fibroids, endometriosis, follicular ovarian cyst, etc.
Irregular sexual activity, refusal to breastfeed, enlarged milk ducts, breast cysts, incorrect or unreasonable intake of hormonal drugs and the late onset of menopause can also provoke the development of mastopathy.
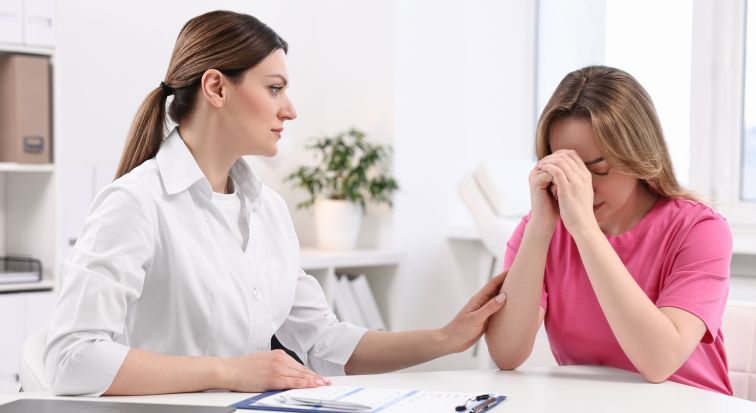
All manifestations of mastopathy can be noticed by a woman herself,
and the appearance of at least one of them is an occasion for urgent consultation with a breast physician.
Patients with mastopathy complain of the following symptoms
dull or aching pain in the chest
breast enlargement
swelling of the gland and its roughening
in rare cases – discharge from the nipples (transparent, greenish, white or bloody)
The first and main way to diagnose diseases of the mammary glands is an independent examination and palpation, allowing a woman to notice one of the above mentioned symptoms of mastopathy and consult a breast physician. The examination conducted by the doctor also begins with palpation, if necessary, an ultrasound of the mammary glands is prescribed – an informative and safe study in which the body is not exposed to radiation.
If necessary, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, thyroid gland is carried out, tests for hormones are prescribed. If problems with the endocrine system or women's health are diagnosed – gynecologist and endocrinologist consultations are appointed.
First of all the treatment of mastopathy is aimed at eliminating the causes that provoked the disease: normalization of prolactin levels, correction of metabolism or restoration of women's health. The therapeutic course includes medication, which is assorted for each patient individually, and lifestyle correction (for example, exclusion of nicotine and alcohol).
Dilated mammary ducts are one of the manifestations of mastopathy, which often causes concern in women. The choice of treatment method depends on the causes of this condition, symptoms and characteristics of the patient's body. We guarantee an individual approach to each patient.
The main stages of treatment:
It is used for minor changes. It includes correction of hormonal balance, taking anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins.
Used in case of neoplasms or complications.
The clinic uses modern methods that ensure minimal trauma.
It is performed only in complex cases when conservative and minimally invasive methods are ineffective.
Enlarged mammary ducts can occur due to hormonal disorders, inflammatory processes, age-related changes or the presence of neoplasms. The cause is precisely determined by diagnostics, ultrasound, mammography or laboratory tests. Treatment depends on the main factor that caused the changes.
Treatment for mastopathy depends on its form and causes. The main methods include hormonal imbalance, anti-inflammatory medications, and lifestyle changes. In complex cases, minimally invasive or surgical techniques are used. A doctor develops a treatment plan individually.
Mastopathy is curable if you consult a doctor in time and follow the prescribed treatment. Early detection of the problem allows you to effectively control it using conservative or minimally invasive methods. Regular preventive examinations will help avoid complications and maintain the health of the mammary glands.