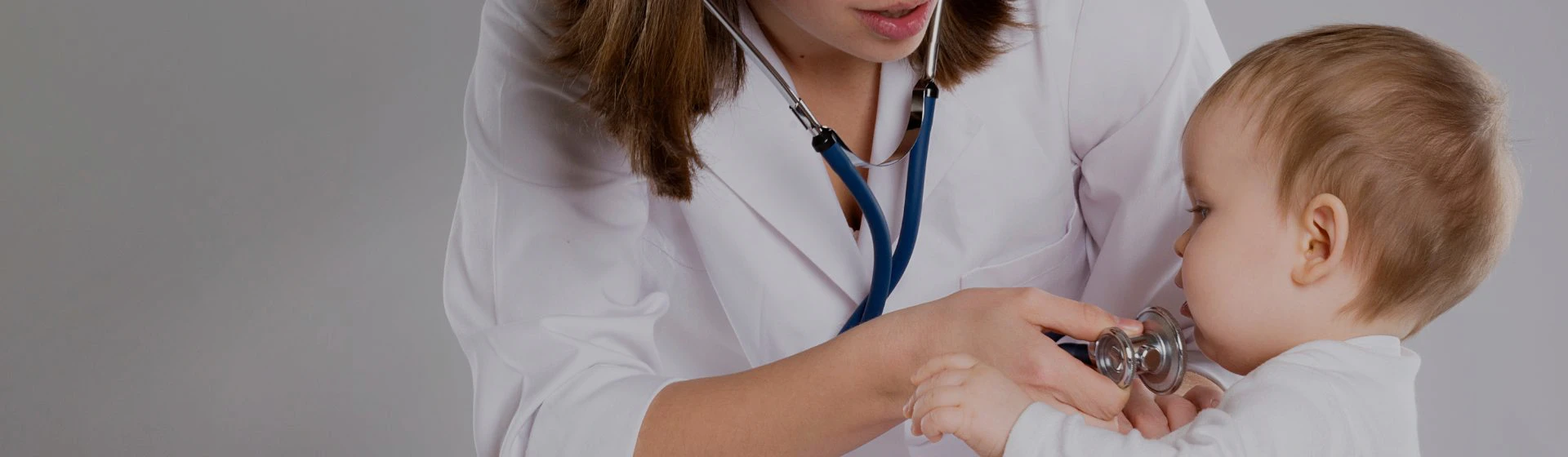
Treatment of children's bronchitis
Treatment of children's bronchitis
A bronchitis is the inflammation of the mucous membrane of bronchi, the part of respiratory ducts of the man, connecting the trachea with lungs. In most cases, the bronchitis is the complication of acute respiratory infections, often affecting children in autumn and winter.

Causes of bronchitis in children
In most cases, the bronchitis appears as the complication of the previous viral infection. The cause of the disease can be the virus itself or the bacterial infection, which attacked the organism, weakened by the virus.
The bronchitis, not associated with viral or bacterial factors, may also develop. It may be the allergic bronchitis (caused by the allergens, penetrating through the mucous membrane of bronchi) or bronchitis, caused by the particles of aggressive chemical substances, penetrating through aggressive chemical substances.
Symptoms of bronchitis in child
The parents not always can distinguish the starting bronchitis from the cold; that is why in case of any cold-related disease, it is recommended that the child is under the care of the pediatrician, who can notice the early signs of bronchitis and distinguish it from ARVI. The earlier the bronchitis is diagnosed and the treatment starts, the easier the progression of the disease will be and the quicker the recovery will be.
The key sign of developing bronchitis is the coughing, which initially can be dry, but then becomes wet, with expectoration of transparent or yellow sputum. The coughing, especially at early stages of the disease, often has the painful nature – the child can cough very often. The cough is accompanied by rales, the nature of which during auscultation can say much to the pediatrician about the progression and degree of severity of the bronchitis.
One more sign of bronchitis is the chest pain, but only the older children (starting from six-seven years) can complain of it, as little children cannot localize the pain feelings by themselves. During the severe stage of bronchitis, the shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat may appear.
During the bronchitis, the temperature may increase; however, it is not excluded that the disease may progress without this symptom – it depends on the condition of the immune system of the child and causes of the development of bronchitis.
Diagnosis and treatment of bronchitis
The bronchitis may progress in the acute and chronic form, which are distinguished by the duration of treatment and pronouncement of symptoms. In most cases, for diagnosing the bronchitis, the doctor just needs to examine the child and auscultate his lungs. The doctor may also order the test of expectorated sputum for microflora and its tolerance to antibiotics.
If there is the probability of development of pneumonia (inflammation of the lungs), the doctor orders the X-ray examination of thoracic organs for ruling out the pneumonia.
The treatment of bronchitis, first of all, depends on the cause of the disease. If it is the virus, the doctor may prescribe the specific anti-viral therapy, if it is the bacteria – antibiotics. In case of the allergic bronchitis, it is required to eliminate the impact of allergen on the organism. In any case, it is indicated to prescribe the expectorant drugs, improving the expectoration of sputum from bronchi, treatment regime compliance, inhalations.
It is difficult to independently determine which specific drugs will be effective and safe for the child; that is why in case of the bronchitis, it is important to consult the pediatrician,visiting the doctor or calling in the specialist.
You can make appointment for consultation with the pediatrician of Oxford Medical clinic by calling us or filling out the form on our website.

Our doctors


Doctor of ultrasound diagnostics



Let's take care
about your health:






