Decreased visual acuity, double vision.
Assessment of the patient's visual acuity using standard charts or electronic devices. This method helps determine the degree of myopia, hyperopia, or other impairments.
Decreased visual acuity, double vision.
The appearance of “floaters” or “fog” in front of the eyes.
Pain, burning, or itching in the eye area.
Redness, tearing, or swelling of the eyelids.
Assessment of the patient's visual acuity using standard charts or electronic devices. This method helps determine the degree of myopia, hyperopia, or other impairments.
A computer-based study that measures the refraction of light in the eye. It allows for accurate detection of myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
Examination of the fundus using a special device. It allows evaluation of the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels. Frequently used for monitoring patients with diabetes or hypertension.
Measurement of intraocular pressure. At Oxford Medical, this test is performed non-contact, making it painless and quick.
Examination of the anterior structures of the eye (cornea, lens, iris) using a slit lamp. The method helps identify inflammation, opacities, or tumors.
A modern diagnostic method that creates layered images of eye tissues. It is used to diagnose glaucoma, retinal dystrophy, detachment, and other conditions.
Yes, it is advisable to remove lenses 2–3 hours before your visit. This allows the ophthalmologist to objectively assess the condition of the cornea, avoid mechanical irritation, and perform accurate diagnostics. If you regularly wear lenses — don’t forget to bring your lens containers.
Yes. If you already wear glasses or have prescriptions or previous exam results, it’s important to bring them. This will help the doctor assess changes in your vision and the effectiveness of prior correction.
No special preparation is needed, but be aware that the doctor may use drops to dilate the pupils for fundus examination. After that, your vision may be temporarily impaired, so it is not recommended to drive or work with documents for 2–3 hours after the visit.
 All advices
All advices Initial consultation is the first stage of the patient’s assessment. During it, the doctor not only conducts diagnostics but also identifies risk factors and determines the need for additional tests or treatment. Thanks to a comprehensive approach, the patient receives a complete picture of their visual health and a clear action plan.
The specialist inquires about symptoms, existing diagnoses, past surgeries, injuries, or comorbidities. It is also important to determine how long the problems have existed and whether they are related to visual strain.
Visiometry, biomicroscopy, and evaluation of the conjunctiva, iris, and cornea are performed. In some cases, tonometry or ophthalmoscopy is conducted. All procedures are painless and comfortable.
If basic information is insufficient, the doctor may prescribe additional tests, such as OCT or ophthalmoscopy with pupil dilation. This allows for accurate diagnosis and ruling out of associated pathologies.
The patient receives a detailed report with treatment advice, vision correction options, or a follow-up plan. If needed, medical therapy is prescribed or surgical treatment is planned.






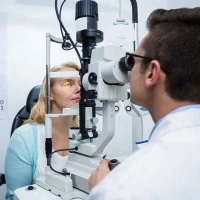
Most patients only visit an eye doctor when their vision worsens. However, regular check-ups are recommended even in the absence of symptoms. In particular, annual or more frequent visits are advised if you have the following risk factors:
Previously diagnosed eye diseases;
Family history (vision problems in close relatives);
Chronic conditions (diabetes, atherosclerosis, nephropathy, hypertension, etc.);
Hormonal disorders;
Eye injuries;
Frequent use of computers and gadgets;
Planning for pregnancy;
Age over 45.
School-aged children should have their vision checked every 6–12 months. Due to increased eye strain, rapid growth, and hormonal changes, the risk of developing myopia and other disorders rises during this period.
Ophthalmologists at our Pechersk branch and other clinics in Kyiv treat eye diseases and other visual system disorders, the most common of which include:
Myopia (nearsightedness) – reduced distance vision.
Hypermetropia (farsightedness) – reduced near vision.
Astigmatism – refractive error due to corneal (or less often lens) shape changes, leading to a lack of a clear focal point.
Strabismus – eye misalignment causing deviation of one or both eyes.
Glaucoma – fluid drainage disorder from the eye, causing increased intraocular pressure.
Cataract – clouding of the lens.
Conjunctivitis – inflammation of the eye’s mucous membrane.
Retinitis – inflammation of the retina.
Neuritis – acute inflammation of the optic nerve.
Retinopathy – retina damage due to vascular disorders and impaired blood supply.
Retinal dystrophy – thinning of tissues due to poor blood flow and nutrition.
Retinal detachment – separation from other eye structures, requiring urgent surgery to prevent vision loss.
Keratoconus – deformation of the cornea.
Chalazion – inflammation of the Meibomian gland, appearing as a small “bump” on the eyelid.
Atheroma – sebaceous gland cyst.
Eye injuries, etc.
At "Oxford Medical" ophthalmologists in Irpen and Kyiv conduct conservative and surgical treatment for eye diseases, as well as selection of glasses and contact lenses for myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
Medical therapy is used for conjunctivitis, retinitis, optic neuritis, and certain other diseases. It can also be prescribed for glaucoma and cataracts as supportive treatment.
Surgical intervention is required for cataracts, glaucoma, retinal detachment, and other irreversible eye conditions. At Oxford Medical, it is performed in a state-of-the-art surgical unit.
Many eye diseases can lead to vision loss, so timely consultation with an eye doctor and early treatment are critically important. Often, this allows the problem to be resolved or the progression of pathology slowed, avoiding irreversible complications.
An ophthalmologist consultation is necessary when vision worsens, “floaters” or “blurriness” appear in front of the eyes, or in the presence of other visual issues.
For preventive purposes, you should be examined at least once a year, and more often if you're over 45 or have risk factors.
During the first visit, the ophthalmologist checks visual acuity and uses computer equipment to measure eye refraction and intraocular pressure. Other tests, such as fundus exam and OCT, are performed if indicated.
If needed, the doctor may also prescribe medication and select glasses or lenses for correction.
During the consultation, the doctor first examines the eyes for redness, discharge, tearing, and other visible symptoms. Then, they assess visual acuity and perform computer-based diagnostics. These are quick, painless procedures that provide precise insight into the eye’s condition.
For fundus examination, which assesses the retina, the doctor may instill drops to dilate the pupils.
Computer diagnostic results are shown as abbreviations and numerical values. For example, R = right eye, L = left eye, Ref = refractometry results, PD = pupillary distance, etc. Only a specialist can correctly interpret these and provide a proper diagnosis.
It’s advisable to come with minimal or no eye makeup, since the doctor may need to hold your eyelids or use drops to dilate your pupils during the diagnostic procedures.
To schedule an ophthalmologist consultation at "Oxford Medical – Kyiv", call our contact center or write to us in the chat on the website.