In most cases, human papillomavirus (HPV) does not cause any symptoms for a long time. Symptoms of HPV in women may include the appearance of papillomas or warts on the genitals, anus, or cervix. In some cases, there may be vulvar papillomatosis, discomfort, burning, or unusual discharge.
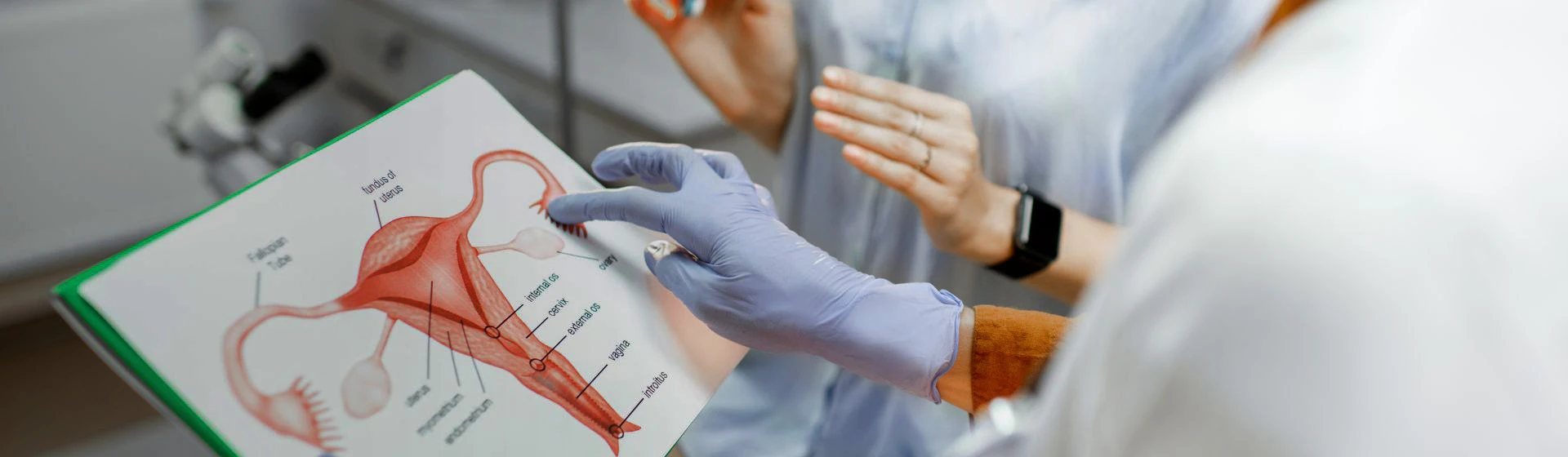
Treatment of HPV in women
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common disease whose pathogen can “live” in the body for a long time and may first manifest on the skin and mucous membranes only years later. There are many types of HPV, each of which manifests differently. Their common main characteristic is provoking the appearance of papillomas and warts. Some types of HPV develop slowly and imperceptibly, eventually leading to a precancerous condition – papillomas transform into cervical dysplasia. In most women and girls, HPV resolves spontaneously. However, if the virus persists, it can trigger the development of condylomatosis, precancerous changes, cervical cancer, and other diseases.
Human papillomavirus in gynecology is one of the most common viral infections, requiring regular examination and medical supervision by a doctor.
Causes of HPV in women
Risk factors for HPV infection include:
-
Sexual activity at an early age;
-
Promiscuous sexual behavior (multiple partners, casual sexual encounters);
-
Weak immune system;
-
Cervical erosion;
-
Infections.
The virus can also be transmitted through household contact. Triggers for the development of HPV often include alcohol and tobacco abuse, severe stress, flu, and gastrointestinal disorders.
It’s important to understand that HPV is very widespread, and all sexually active populations are at risk. HPV is transmitted through any contact with the skin and mucous membranes of a carrier. The virus does not enter the bloodstream or other tissues and organs; it replicates in the deeper layers of the skin. Once the virus reaches the infected epithelium and surfaces, it becomes contagious. Another frequent cause of HPV transmission is visiting public places with high humidity: baths, saunas, swimming pools, etc.
Human papillomavirus: symptoms in women
HPV symptoms depend on the virus type, although in most infected individuals, it remains asymptomatic.
Signs of human papillomavirus in women:
-
Pain and burning in the genital area;
-
Pain during sexual intercourse;
-
Unusual vaginal discharge.
In addition, genital warts often appear on the genitals and in the anal area. Weeks or even years may pass from the moment of infection to the appearance of these warts. Genital warts are small wart-like growths of slightly pink or flesh color, ranging from 1 mm to several centimeters. Over time, they can grow and turn into multilayered formations. Depending on the immune system condition, warts may proliferate, remain unchanged for a long time, or disappear on their own.
Types of HPV
After infection, HPV may exist in the human body in two forms:
-
Latent form – The viral DNA does not integrate into the cell DNA and does not cause pathological processes. The infected person has no symptoms, but the infection is confirmed through laboratory diagnostics.
-
Productive form – The infection actively develops, causing clinical symptoms. In particular, patients may develop papillomas and condylomas.
If not treated in time, HPV in women can lead to:
-
Cervical erosion;
-
Cervical dysplasia;
-
Malignant tumors.
According to the WHO, HPV types 16 and 18 cause cervical cancer and precancerous conditions in 70% of cases. The virus has also been linked to cancers of the vulva, vagina, anus, penis in men, and oropharynx.
About 30 types of sexually transmitted HPV are considered potentially oncogenic. HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 50, 59, 64, 68, and 70 are classified as high-risk, while types 30, 35, 45, 52, 53, 56, and 58 are medium-risk. Others are associated with a low risk of cancer. For instance, types 6 and 11 most often cause genital warts.
HPV Diagnostics
HPV diagnosis begins with an examination of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as clarification of the patient’s complaints. Women are indicated for examination of the vagina and cervix, colposcopy, cytological testing, and, when indicated, biopsy.
To confirm the infection and determine its type, tests for papillomavirus are performed, allowing assessment of the presence of HPV, its oncogenic risk, and viral load. The most accurate laboratory diagnostic method is the Digene test, which makes it possible to detect the virus, determine its type, and assess the degree of malignancy.
Methods of HPV Treatment in Women in Kyiv
The treatment strategy for human papillomavirus in women is determined by the HPV type, its oncogenic risk, the presence of clinical manifestations, and examination results. The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the manifestations of the infection, reduce the viral load, and prevent the development of complications. To date, there is no method that can completely eliminate the papillomavirus from the body; however, properly selected treatment helps control the course of the infection and achieve stable remission.
As part of treatment, removal of genital papillomas in women caused by viral activity is also performed. Modern methods are used, including cryotherapy and electrocoagulation, which allow genital papillomas to be removed with minimal trauma to surrounding tissues.
If precancerous changes or malignant neoplasms are detected, the treatment strategy is determined individually and may involve surgical intervention followed by medical follow-up.
Human Papillomavirus During Pregnancy
Detection of the human papillomavirus during pregnancy is a common situation and in most cases does not pose a direct threat to the course of pregnancy or fetal development. HPV often persists in the body in a latent form and is detected during routine examinations in pregnancy, when a woman undergoes extended diagnostic testing.
Against the background of hormonal changes and a physiological decrease in immune defense, more active manifestations of the virus are possible, including the appearance or enlargement of genital papillomas.
During pregnancy, active methods of HPV treatment are generally not used. The main emphasis is placed on medical monitoring. Removal of papillomas on the labia or other areas is performed only when there are medical indications, such as rapid growth of lesions, bleeding, or pronounced discomfort.
The presence of HPV is not an indication for cesarean section. The method of delivery is determined by the obstetrician-gynecologist, taking into account the woman’s general condition and obstetric indications.
After childbirth, when hormonal balance stabilizes, the doctor may recommend further examinations and, if necessary, treatment.
HPV prevention in women
You can protect yourself against the most common and dangerous types of HPV through vaccination. Inactivated vaccines covering 2, 4, or 9 HPV types are used for this purpose.
The WHO recommends vaccination at the age of 9 to 14. However, both women and men may get vaccinated later — optimally before the age of 26.
In addition to vaccination, there are other preventive methods, referred to as secondary prevention. They aim to reduce the risk of infection and recurrence.
Recommended HPV prevention measures:
-
Use barrier contraception (although it does not guarantee 100% protection);
-
Maintain a monogamous relationship;
-
Undergo a gynecological check-up with colposcopy and a Pap test once every 6–12 months;
-
Strengthen the immune system;
-
Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption.
For patients infected with high-risk HPV types, the doctor may recommend an individualized prevention program. The most important aspect is regular cervical screening and testing.
Advantages of human papillomavirus treatment in Kiev at Oxford Medical
"Oxford Medical" offers everything necessary for successful treatment:
-
High qualification of specialists: the clinic’s gynecologists are proficient in all effective diagnostic and treatment methods, both surgical and conservative;
-
Use of unique treatment techniques;
-
State-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment equipment;
-
Rehabilitation programs;
-
Individual approach to each patient;
-
Comfortable conditions during your stay at the clinic.
At Oxford Medical you can receive high-quality medical services in Kyiv and Irpen. The latest equipment, experienced doctors and a friendly atmosphere – we have everything for accurate diagnostics and effective treatment.
Services of a Private Clinic in Kyiv: Cost of HPV Treatment for Women at “Oxford Medical”
The cost of treating human papillomavirus infection in women is determined by the scope of required medical services. The need for treatment and the therapeutic approach are determined individually after examination and assessment of test results.
You can review current prices for medical services in Kyiv at the “Oxford Medical” clinic on the website or by contacting the contact center. More detailed information about treatment options and costs will be provided by the doctor during the consultation.
You can book an appointment at a convenient time by phone or via the online appointment form on the website.
Frequently asked questions:
How does HPV manifest itself in women?
What causes papillomas?
Papillomas appear as a result of the activation of the human papillomavirus in the body. The cause of papillomas is most often associated with a decrease in immune defense, hormonal changes, stress or concomitant infections. After infection, the virus can remain latent for a long time without external signs.
How to remove the papilloma virus from the body?
Currently, there are no methods that allow you to completely remove the papillomavirus from the body. Medical care is aimed at controlling the infection, reducing the viral load and eliminating clinical manifestations. With stable immunity, HPV may not manifest itself for a long time and not cause complications.
Can human papillomavirus be cured permanently?
Human papillomavirus is not an infection that can be completely eliminated with medication. Treatment is aimed at eliminating symptoms, preventing complications, and regular monitoring. In many women, under favorable conditions, the immune system suppresses the activity of the virus, which allows for long-term remission.
Which doctor should I see for papillomas?
When papillomas appear, a woman should consult a gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, prescribe HPV tests if necessary, and determine further management tactics. Self-removal of papillomas or ignoring symptoms is not recommended, as this may lead to complications or miss dangerous changes.
How to remove papillomas on the genitals?
Removal of genital warts is performed in a medical facility after a doctor's examination. Depending on the clinical situation, hardware methods are used, in particular cryotherapy or electrocoagulation. The method is chosen individually, taking into account the localization of the formations, their size and the general condition of the patient.
What happens if the papilloma virus is not treated?
In the absence of medical control, HPV can remain active for a long time and lead to the progression of the disease. In some cases, this is accompanied by the appearance of multiple papillomas, the development of cervical dysplasia or other precancerous changes. Regular examinations allow for the timely detection of dangerous conditions.
How is papillomavirus transmitted?
Human papillomavirus is transmitted mainly through skin or mucous membrane contact, most often through sexual contact. Infection is also possible through micro-damage to the skin in everyday life. The use of barrier contraception reduces the risk of infection, but does not provide complete protection.
How to have sex with HPV?
The presence of HPV is not an absolute contraindication to sexual activity. It is recommended to use barrier methods of contraception and regularly see a doctor. During the period of active manifestations or procedures, the doctor may advise temporary restrictions to reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to a partner.
How to treat papillomavirus types 16 and 18?
HPV type 16 in women, as well as type 18, are of high oncogenic risk, therefore they require particularly careful monitoring. Treatment includes regular gynecological examinations, laboratory monitoring and, if necessary, removal of pathological formations. Tactics are determined individually after diagnosis.
Our doctors


Specialist in aesthetic gynecology.





Let's take care
about your health:






