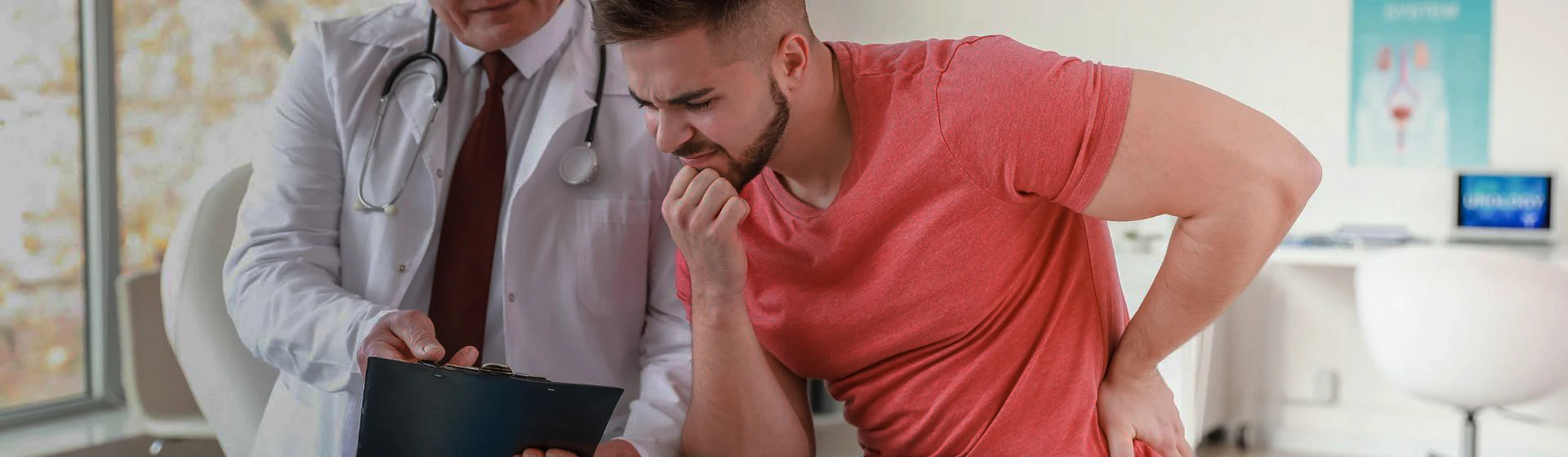
Vesiculitis is also referred to as spermatocystitis — a term derived from the Latin words sperma (sperm) and cystis (bladder), which directly indicates involvement of the seminal vesicles.
The seminal vesicles are paired organs of the male reproductive system located on both sides of the prostate gland. They synthesize fructose, ascorbic acid, and proteins — substances necessary for sperm formation — and also participate in the process of ejaculation.
When inflammation develops, swelling of the seminal vesicles and an increase in their size occur. As a result, they may exert pressure on the prostate gland and the urethra, leading to impaired function and the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
Diagnosis and treatment of vesiculitis are carried out by urologists or andrologists. In Kyiv, it is possible to receive a consultation with an experienced specialist, undergo laboratory tests, and complete the necessary examinations using high-precision equipment at the medical center Оксфорд Медікал.
Most often, vesiculitis develops against the background of inflammation or infection in other organs of the genitourinary system, but it may also occur as an independent condition.
The most common causes include:
-
urethritis — inflammation of the urethra;
-
cystitis — inflammation of the urinary bladder;
-
prostatitis — inflammation of the prostate gland;
-
sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, and others);
-
chronic inflammatory diseases of any localization (ENT diseases, etc.);
-
congenital abnormalities of the genitourinary system;
-
decreased tone of the seminal vesicles;
-
dilation of hemorrhoidal veins, among others.
The risk of developing the disease increases in the presence of weakened immunity, hypothermia, injuries to the groin area, frequent constipation, physical inactivity (leading to pelvic blood congestion), high sexual activity or prolonged abstinence, as well as harmful habits.