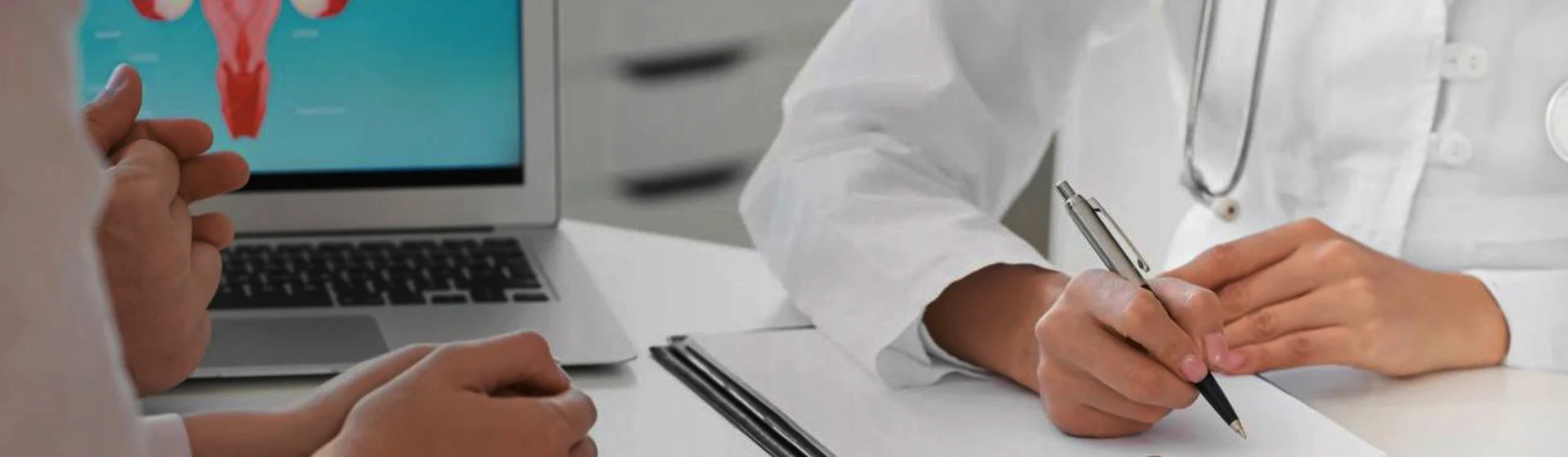
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome is selected individually and depends on the clinical picture, the woman’s age, the presence of concomitant disorders, and reproductive plans.
Conservative treatment
Conservative therapy is the main method of treating PCOS in most patients. It is aimed at correcting hormonal imbalance, normalizing the menstrual cycle, and reducing manifestations of hyperandrogenism.
Within the conservative approach, the following may be used:
- hormonal medications to regulate the menstrual cycle;
- agents to reduce androgen levels;
- pharmacological correction of carbohydrate metabolism disorders in the presence of insulin resistance;
- symptomatic treatment of associated manifestations.
The treatment regimen is determined by the doctor individually after examination and may be adjusted depending on the dynamics of the patient’s condition.
Surgical treatment
Surgical methods of treatment are used on a limited basis, particularly in cases of ineffectiveness of conservative therapy. The purpose of surgical intervention is to restore ovulatory function rather than to radically cure the syndrome.
Modern operations are performed using minimally invasive techniques, with maximal preservation of ovarian tissue. The appropriateness of surgical treatment is determined individually by the doctor after evaluating the results of medical therapy.
Long-term follow-up and monitoring
PCOS belongs to chronic conditions, therefore treatment is not limited to a single course of therapy. Regardless of the chosen method, regular follow-up with a doctor is recommended to monitor hormonal levels, the menstrual cycle, and overall health.
Effective treatment of PCOS involves a combination of a properly selected therapy method and systematic medical monitoring, which helps reduce disease manifestations and prevent the development of complications.