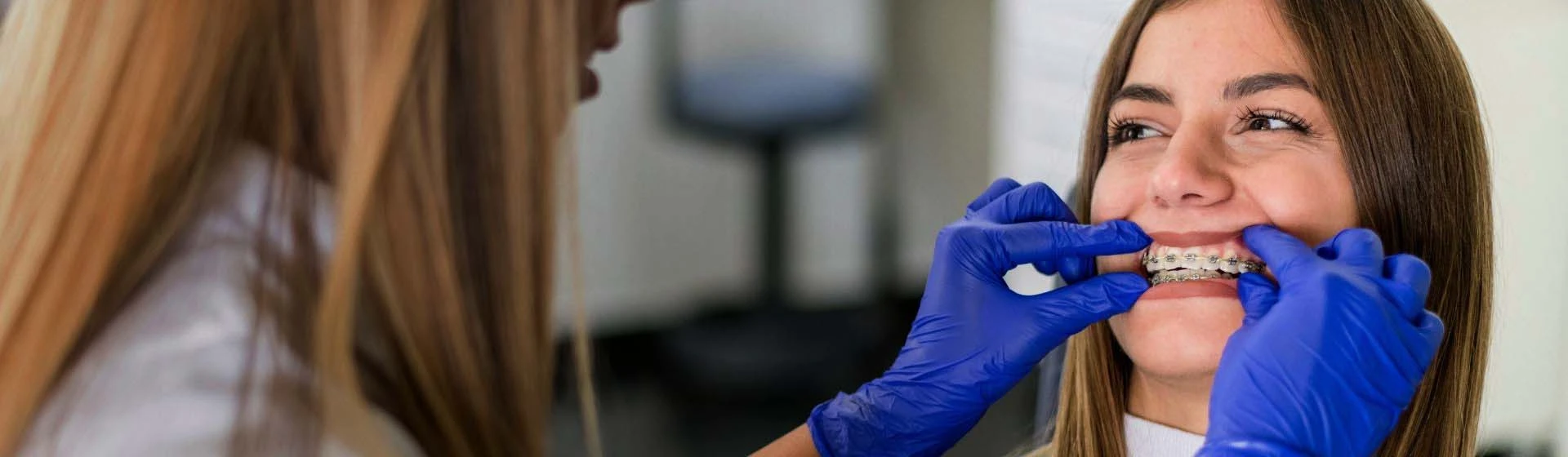
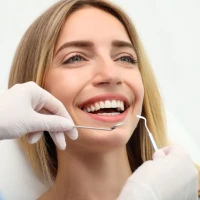
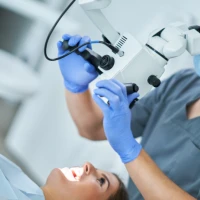
Bite assessment begins with an orthodontic consultation. The doctor evaluates the position of the teeth, the relationship of the jaws, the character of the closure and the functioning of the temporomandibular joint. Such an examination makes it possible to detect early signs of deviations, but instrumental examinations are always required for accurate diagnosis.
The next stage is a photo protocol – a series of intraoral and extraoral photographs that help analyse facial symmetry, profile and features of the smile. In parallel, intraoral scanning or impression taking is performed to create digital models of the jaws. This makes it possible to accurately assess the position of the teeth and the character of the closure.
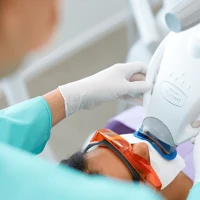
Radiological examinations are mandatory. Panoramic radiography (OPTG) shows the general condition of the teeth, roots, bone tissue and the presence of tooth germs. To analyse the relationship of the jaws, the direction of growth and assess facial proportions, cephalometric radiography (TRG) in lateral projection is used. In complex cases, computed tomography (CT) may be performed, which provides a three-dimensional image and allows detailed study of jaw anatomy.
Comprehensive diagnostics ensures accurate assessment of the bite and makes it possible to choose the most effective treatment plan for each patient.