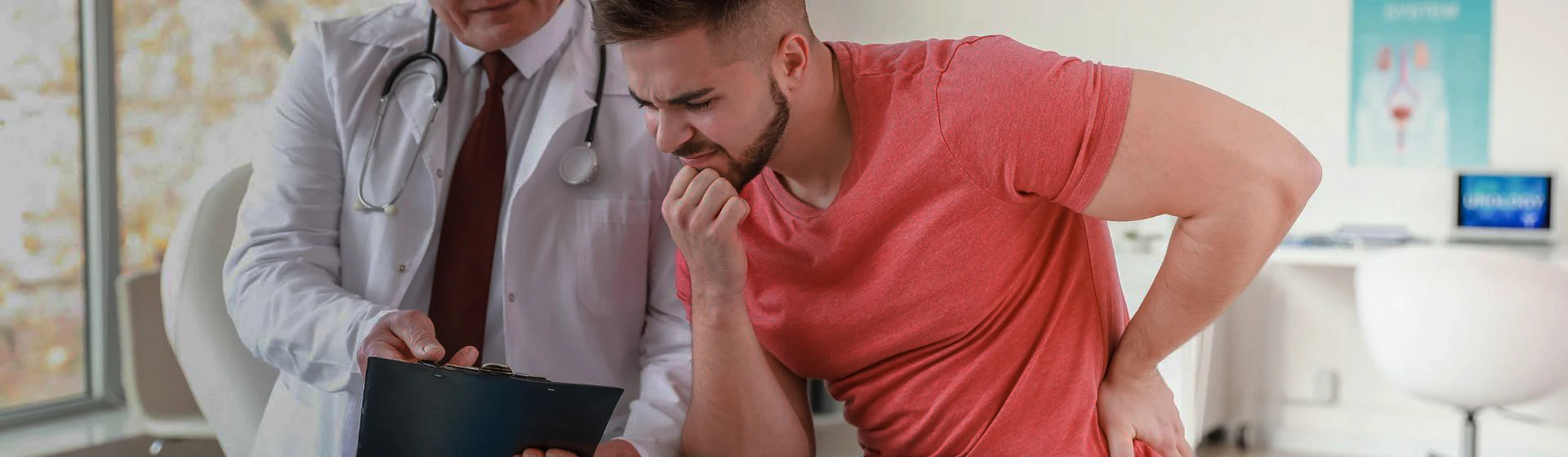
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis that develops mainly as a complication of other diseases of the reproductive system or general illnesses (such as acute respiratory viral infections, etc.). It is accompanied by redness and swelling of the scrotum on the side of the inflammatory process, severe pain, elevated body temperature, and other symptoms.
The epididymis is a paired organ. It appears as a long and narrow duct and is located on the posterior surface of the testicle. In the epididymis, sperm cells that have left the testicle mature over a period of two weeks, after which they move into the spermatic cord. When inflammation of the epididymis occurs, this process is disrupted, which leads to a deterioration in sperm quality and an increased risk of infertility. However, this complication is more typical of the chronic form of the disease. The acute form is successfully treated with medication, but the effectiveness of therapy depends on how early treatment is initiated.