Hemorrhoid treatment
What is hemorrhoids?
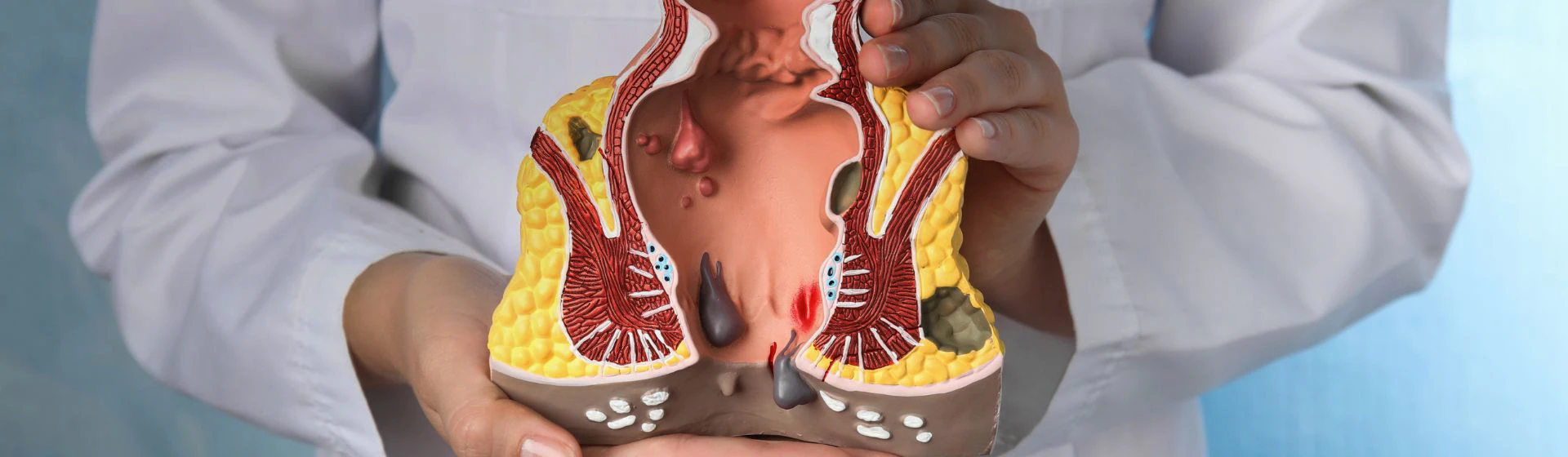
Hemorrhoids is a disease affecting the veins of the rectum. With impaired blood circulation in the pelvis, a significant increase in intra-abdominal pressure, suffers nutrition of the organs that are located here (including the rectum). There is stagnation in the vessels, their expansion and the formation of hemorrhoidal nodes.
At first, hemorrhoids may not manifest themselves in any way. However, the nodes are constantly traumatized by the passage of fecal matter, increased pressure in the pelvis, which leads to unpleasant symptoms:
- itching;
- heaviness, pressure, pain in the anus;
- defecation disorders (constipation);
- sensation of a foreign body in the sphincter area;
- appearance of blood in the stool;
- prolapse and impingement of nodes.
If you do not establish a correct diagnosis in time and do not start treatment, complications and pathologies develop. The most formidable complications are considered bleeding from hemorrhoidal nodes, their thrombosis and necrosis.
Depending on the course of the disease, acute and chronic hemorrhoids are distinguished. Acute develops within a few days and is characterized by a violent course. In the chronic form, the manifestations of the disease are minimal, which carries a hidden danger. Patients do not go to the doctor for a long time, ignore the problem, which often leads to the development of complications.
Causes of hemorrhoids
The main provoking factors for hemorrhoids, according to proctologists, are:
-
work and physical activity associated with lifting heavy objects;
-
childbirth;
-
sedentary work;
-
improper diet;
-
chronic constipation;
-
frequent diarrhea;
-
obesity;
-
alcohol abuse;
-
cycling, horseback riding;
-
increased intra-abdominal pressure;
-
old age.
Stages of hemorrhoids
Specialists distinguish 4 stages of hemorrhoid development:
- First stage – a slight enlargement of hemorrhoidal nodes is observed, which causes discomfort and occasional mild bleeding after defecation.
- Second stage – during straining, the hemorrhoidal nodes prolapse but reposition themselves afterward; in addition, the patient begins to experience itching and discomfort in the anal area.
- Third stage – after prolapse, the hemorrhoidal nodes are repositioned manually and remain in the anal canal until the next defecation; heavy bleeding becomes more frequent.
- Fourth stage – the hemorrhoidal nodes prolapse and can no longer be repositioned, causing the patient constant discomfort and pain (it becomes uncomfortable to sit, stand up, or perform active movements), and spontaneous bleeding may occur.
In stages 1 and 2, conservative treatment methods are sometimes used, while in stages 3 and 4, hemorrhoids can only be removed surgically.
Treatment methods
Proctology offers a wide range of conservative and minimally invasive technologies for treating hemorrhoids.
Conservative Therapy for Hemorrhoids
It is appropriate only in the early stages of the disease. It includes:
- changes in diet;
- avoiding a passive lifestyle and heavy lifting;
- use of local remedies (gels, suppositories, ointments);
- prescription of systemic pain relievers in the presence of severe pain;
- use of agents that strengthen the walls of venous vessels.
With correct, individualized drug selection and timely initiation of treatment, the condition can be eliminated fairly quickly.
Infrared Photocoagulation
This method is based on the sclerosing of the hemorrhoidal node using an infrared thermal beam. Cauterization of the node's base deprives it of nutrition, leading to its subsequent necrosis. A few hours after the procedure, the patient can leave the clinic. Complete rejection of the node usually occurs within 5–10 days.
Infrared coagulation can be used in stages 1–2 of hemorrhoids.
Ligation with Latex Rings
The technology involves the following steps:
- a special anoscope is used to insert a sensor that shows the blood flow in the vessels of the area;
- the vessel supplying the node is identified and ligated;
- the mucous membrane above the node is stitched, which leads to its return to the physiological position.
Anesthesia is used to insert the sensor into the anal sphincter. The procedure can be performed at any stage of hemorrhoids.
Laser Treatment of Hemorrhoids
A light guide and thin laser are inserted into the rectum. The laser beam acts inside the pathological formation, excluding effects on adjacent tissues.
Transanal Resection (Longo Procedure)
In advanced stages of hemorrhoids and in the presence of complications, surgical treatment according to Longo is necessary. The operation is performed under anesthesia and consists of circular excision of the mucous membrane above and around the node. This deprives the pathological area of blood supply, leading to the complete disappearance of the nodes.
Choosing a treatment method
The choice of hemorrhoid treatment method depends on several factors:
- The stage of the condition and its characteristics (external or internal hemorrhoids).
- Whether the process is acute or chronic.
- Presence of comorbid pathologies of internal organs.
- Individual characteristics of the patient (age, pain threshold, work conditions, etc.).
- Availability of special equipment in the clinic and the doctor's skills.
The treatment course and hemorrhoid removal technique are selected after a comprehensive examination and consultation with a proctologist.
Treatment of Acute Hemorrhoids
A course of conservative therapy is required. It is aimed at relieving symptoms and promoting the transition of the disease into a latent phase. Only after this can the hemorrhoidal nodes be removed.
Treatment of Chronic Hemorrhoids
The treatment strategy for this form of the condition directly depends on its stage. In the early stages, conservative treatment is possible, which can eliminate unpleasant symptoms and prevent further progression of hemorrhoids.
In stages 2–3, preference is given to minimally invasive methods that not only eliminate the source of the problem but also do not affect the patient's quality of life.
In advanced cases and in the presence of complications, hemorrhoid treatment is possible only with surgical intervention and often requires inpatient care. That is why it is very important to consult a proctologist in a timely manner.
What happens during a proctologist appointment?
When unpleasant symptoms appear, you need to see a proctologist. A consultation with this specialist follows a specific algorithm:
-
Patient interview. The doctor needs to find out what is bothering the patient and how long the problem has existed.
-
Digital rectal examination. This allows assessment of the rectum's condition, presence of pathological formations, or blood.
-
If the doctor detects a pathological formation, anoscopy is performed. Using a special device equipped with a camera, the rectum is examined. The image is displayed on a screen, allowing full assessment of the rectal mucosa and determination of the nature of the formation (hemorrhoidal node, polyp, tumor, etc.).
All this allows the proctologist to make a correct diagnosis and choose an appropriate treatment course or surgical method.
Hemorrhoid prevention
To prevent hemorrhoids, it is recommended to:
- eat a balanced diet;
- lead an active lifestyle;
- avoid excessive strain and frequent heavy lifting;
- carefully maintain intimate hygiene.
If hemorrhoids appear, to prevent the disease from progressing, it is also recommended to temporarily refrain from swimming, cycling, horseback riding, heavy lifting, gym workouts, and consuming spicy or hot foods.
Our doctors






Let's take care
about your health:






