-
Traumatic tear due to sports or everyday injuries.
-
Degenerative changes in the posterior horn of the medial meniscus, which over time lead to the formation of tears.
-
Old meniscus damage that was not treated in a timely manner and causes discomfort or limited mobility.
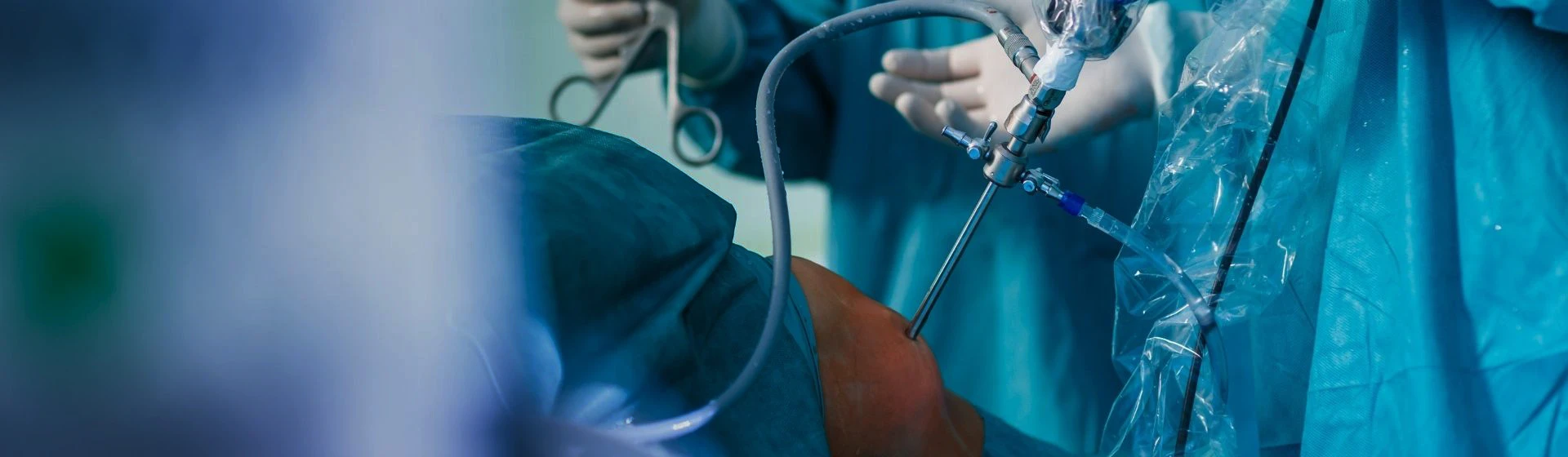
Arthroscopy of the meniscus
Meniscus arthroscopy in Kiev
Meniscus arthroscopy– is a minimally invasive surgery aimed at treating damage to the meniscus of the knee joint. The meniscus – is a cartilage pad located between the femur and tibia. It performs the functions of shock absorption and stabilization of the joint.
During the meniscus operation, the surgeon inserts an arthroscope into the knee joint. It is an elastic tube with a diameter of 4-5 mm, equipped with an optical system. The image from it is transmitted to the monitor screen with a magnification of 40-60 times. Thanks to this technology, the surgeon can examine the tissues, detect damage and treat pathologies such as meniscus tears, degenerative changes or old meniscus damage.
After meniscus arthroscopy, the patient can walk and lean on the knee for 1-3 days, and work capacity is restored, as a rule, within 2-4 weeks, which is much less than after traditional surgery.
At the «Oxford Medical» clinic, meniscus arthroscopy is performed by highly qualified orthopedic surgeons and traumatologists with many years of experience in performing minimally invasive interventions. To ensure the highest accuracy and effectiveness of treatment, modern arthroscopic systems are used, which allow procedures to be performed with minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Thanks to the combination of professional experience of doctors and the latest equipment, our patients receive:
-
the most accurate diagnosis of the condition of the knee joint;
-
a gentle approach to surgery that reduces the risk of complications;
-
a shortened and easier rehabilitation period that allows you to return to your usual life faster.
Do you have problems with your knee and need surgical treatment? Make an appointment with an orthopedic traumatologist at «Oxford Medical». Our specialists will provide high-quality medical care and ensure comfort during your stay in the clinic.
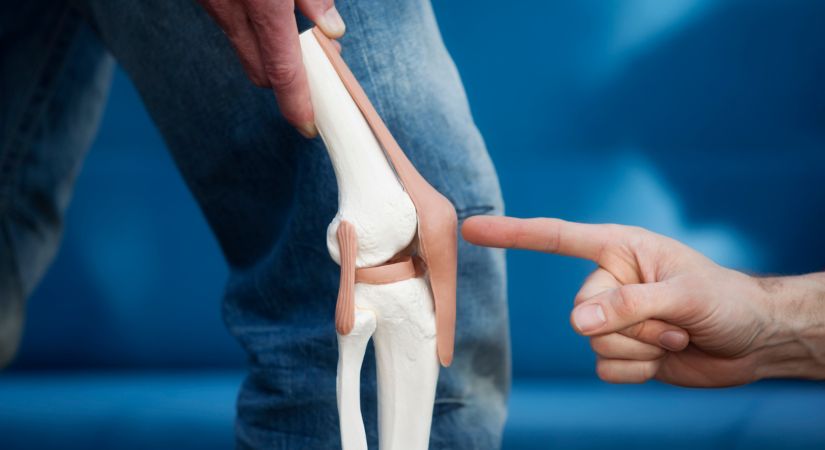
When is meniscus arthroscopy necessary?
The choice in favor of meniscus arthroscopy is made after a detailed diagnosis, which includes a clinical examination and instrumental studies.
Indications for meniscus arthroscopy may be:
Meniscus tear
Chronic knee pain
-
Persistent pain that persists even after conservative treatment (physiotherapy, medication).
-
Pain when bending, extending, or rotating the knee.
Joint locking
A feeling of "locking" in the knee, making movement difficult. This may be due to the presence of fragments of the damaged meniscus, which interfere with the normal functioning of the joint.
Fluid buildup in the joint (synovitis)
Recurrent knee effusion caused by meniscus damage.
Degenerative changes of the meniscus
Age-related or chronic changes accompanied by destruction of the cartilage structure and pain.
Sports injuries
Meniscus tears in professional athletes or people who are actively involved in sports, for the fastest possible return to physical activity.
Suspected meniscus injury
Difficult cases are when other diagnostic methods (ultrasound, X-ray, CT) have not given a clear result, and it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Preparing for surgery
Before knee joint arthroscopy careful preparation is carried out, which includes:
-
Consultation with an orthopedic doctor who will explain the essence of the operation, answer all questions and talk about rehabilitation.
-
Instrumental examinations (ultrasound, X-ray, CT) to accurately determine the damage.
-
Blood tests, ECG and consultation with an anesthesiologist to choose the optimal type of anesthesia.
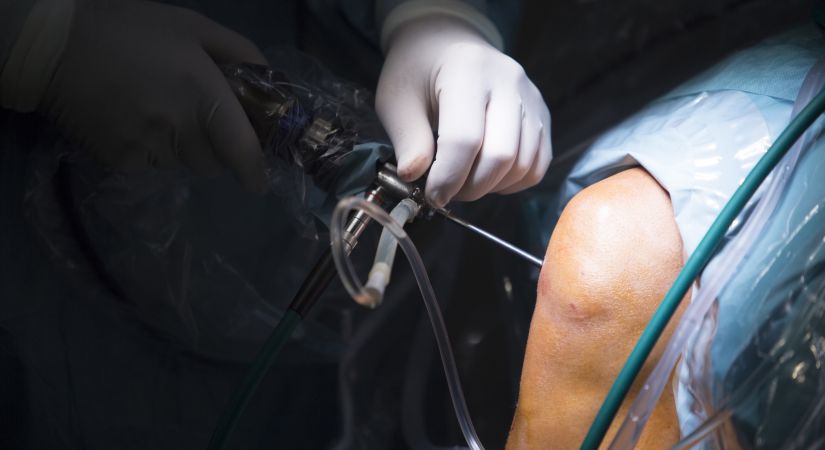
How is the operation performed?
Arthroscopic meniscectomy is one of the safest and most effective procedures for treating the meniscus.
The operation consists of several stages:
1. Introduction of anesthesia
The patient is given anesthesia to ensure pain-free and comfortable surgery on the meniscus of the knee. Spinal anesthesia is most often used, which “turns off” the sensitivity of the lower body, but allows you to remain conscious.
2. Creating access to the joint
The surgeon makes several small incisions in the skin in the projection of the
knee joint (usually 2-3). The incisions are very small - up to 5 mm.
-
The first incision is used to insert an arthroscope - a thin optical device with a camera that
transmits an image to a screen. This allows the doctor to examine the internal structure of the joint in detail. -
The second and third incisions are needed to insert surgical instruments with which the surgeon performs the main
therapeutic manipulations.
3. Diagnosis and treatment
After inserting the arthroscope, the surgeon examines the joint from the inside to confirm the diagnosis and assess the condition of the meniscus and surrounding structures. Depending on the type of damage, the following actions are performed:
-
Partial meniscus resection (partial removal).
It is performed when part of the meniscus is damaged, but the rest of the tissues are in satisfactory condition. The surgeon removes only the damaged part, preserving the healthy fragment of the meniscus to maintain its shock-absorbing function. Partial resection of the medial
meniscus is used to treat a tear of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus or other partial injuries. -
Complete resection of the medial or lateral meniscus (complete removal of the meniscus). It is used in cases where the meniscus is severely damaged and its restoration is impossible. Meniscectomy is used to treat old meniscus injuries or severe degenerative changes.
-
Repair of the meniscus (suturing). It is performed if the nature of the meniscus tear allows for successful restoration of its structure (for example, a tear in an area with good blood supply). In the case of a meniscus tear, suturing surgery makes it possible to preserve the integrity of the meniscus and its function.
4. Completion of the operation
After the damage is repaired, the doctor checks to see if the joint has been properly restored to function. The arthroscope and instruments are removed, and the incisions are sutured or covered with special bandages. A sterile dressing is usually applied to protect against infection.
Rehabilitation after meniscus arthroscopy
After meniscus arthroscopy, it is important for the patient to follow the doctor's recommendations to ensure successful restoration of the function of the knee meniscus. The duration of rehabilitation depends on the complexity of the operation, the type of damage and the patient's general health.
The postoperative period includes several stages, each of which is aimed at alleviating the patient's condition, healing tissues and returning to an active life.
The first hours after surgery
-
Clinical follow-up. After the surgery, the patient is monitored by medical staff for a while to ensure that the anesthesia has gone smoothly and that the patient is in a stable condition. Most patients can leave the clinic the same day.
-
Pain and swelling. In the first few hours, you may experience mild pain and swelling in the area of the surgery. Painkillers and cold compresses are used to reduce this.
The first days after surgery
-
Limiting loads. It is recommended to minimize physical activity, especially avoiding prolonged standing or walking. The leg should be kept in an elevated position to reduce swelling.
-
Using crutches. In some cases, the doctor may recommend crutches to reduce the load on the operated leg.
-
Dressing and suture care. The incisions through which the arthroscope and instruments were inserted are small, but require careful care. The sutures or special plasters remain for 7-10 days, after which they are removed by the doctor.
Beginning of rehabilitation (1–2 weeks)
-
First exercises. A few days after surgery, the patient may be prescribed light exercises to restore mobility of the knee joint. These may include flexion and extension of the leg in a supine position and isometric exercises to strengthen the thigh muscles.
-
Physiotherapy. During this period, procedures aimed at reducing swelling, pain relief and stimulating blood circulation, such as magnetotherapy, lymphatic drainage and ultrasound therapy, play an important role.
The main stage of rehabilitation (3–6 weeks)
-
Regaining strength and flexibility. At this stage, rehabilitation focuses on strengthening muscles, stabilizing the joint, and regaining full range of motion. The patient may be advised to do resistance exercises to strengthen muscles and balance exercises to improve coordination.
-
Gradual weight gain. The patient is allowed to return to light physical activity, such as walking short distances.
Return to an active lifestyle (6–12 weeks)
Full physical activity. After 2-3 months, the patient can return to their usual level of activity, including sports, unless the doctor has indicated contraindications.
Meniscus surgery: price at the Oxford Medical clinic
By choosing the Oxford Medical clinic, patients receive treatment in a modern surgical hospital. Thanks to high quality standards, modern equipment and a professional team, Oxford Medical becomes the optimal choice for the treatment of knee joint injuries. Book a consultation today! Our specialists will be happy to help you take an important step towards restoring the health and mobility of your knees!
The cost of the operation may vary depending on the complexity of the case, the type of intervention (partial resection, suturing, removal of the meniscus), and the duration of the hospital stay. You can find out the prices here. The doctor will provide you with more detailed information about the features of the treatment and the cost during the consultation.
Make an appointment at a time convenient for you by phone or via online chat on the website.
Frequently asked questions
What should you not do after meniscus surgery?
After surgery, you should avoid physical exertion, jumping, running, lifting weights, and standing for long periods of time. You should not violate your doctor's recommendations, ignore rehabilitation exercises, or forget about suture care. You should also avoid hypothermia of the knee and sudden movements.
How long does it take for a meniscus to heal?
Healing time depends on the type of surgery. After a partial resection, full recovery takes 4-6 weeks. In the case of meniscus suturing, the process can take up to 3-6 months. The speed of healing is influenced by the individual characteristics of the patient and compliance with the rehabilitation program.
Our doctors




Let's take care
about your health:






