a round, painless or slightly painful lump in the jaw area, under the tongue, or near the ear
Used for small asymptomatic cysts
Salivary gland cysts — are benign tumors that can occur at any age and gradually increase in size. They usually do not cause pain, but can cause swelling, speech disorders, swallowing, or changes in facial contours. An effective treatment method is surgical removal of the cyst, which is performed using minimally invasive techniques.
At the medical center «Oxford Medical» in Kyiv, patients have access to accurate diagnostics and safe removal of salivary gland cysts. Don't delay your treatment — make an appointment today.
A salivary gland cyst is a fluid-filled sac that occurs when salivary flow from the gland's duct is obstructed. It can occur in the major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, sublingual) or in the minor salivary glands located in the mouth.
The most common type is a retention cyst. It forms when a salivary duct becomes blocked and saliva accumulates within the tissues. If the cyst occurs directly under the tongue, it is called a ranula or sublingual cyst.
These cysts are usually benign, but they can cause discomfort, affect speech and chewing, become infected, or become infected.
The main reason is impaired salivary duct patency.
This can occur due to:
mechanical injury to the mucous membrane (impacts, bites, dental procedures);
presence of microliths (small stones in the ducts);
congenital anomalies of the ductal system;
chronic inflammation of the salivary glands;
tumors or compression from the outside.
In children, ranulosa cysts are often congenital in origin. In adults, they often occur after injuries or inflammation.
A separate type is a retention cyst of the minor salivary gland, which can appear
on the inner surface of the lips, cheeks, or palate. It looks like a small transparent
ball and sometimes bursts on its own, but later forms again.
Symptoms depend on the size, location, and duration of the cyst.
The most common symptoms:
a round, painless or slightly painful lump in the jaw area, under the tongue, or near the ear
foreign body sensation in the mouth
edema or swelling that increases when eating
speech or swallowing disorders
saliva with pus in case of infection
To accurately establish the diagnosis, the doctor conducts a clinical examination and, if necessary, prescribes additional studies:
ultrasound examination (US);
computed tomography (CT) for visualization of deep formations;
puncture of the cyst contents;
histological examination after removal.
An experienced maxillofacial surgeon determines the type of formation, excludes a tumor nature and selects the optimal treatment tactics.
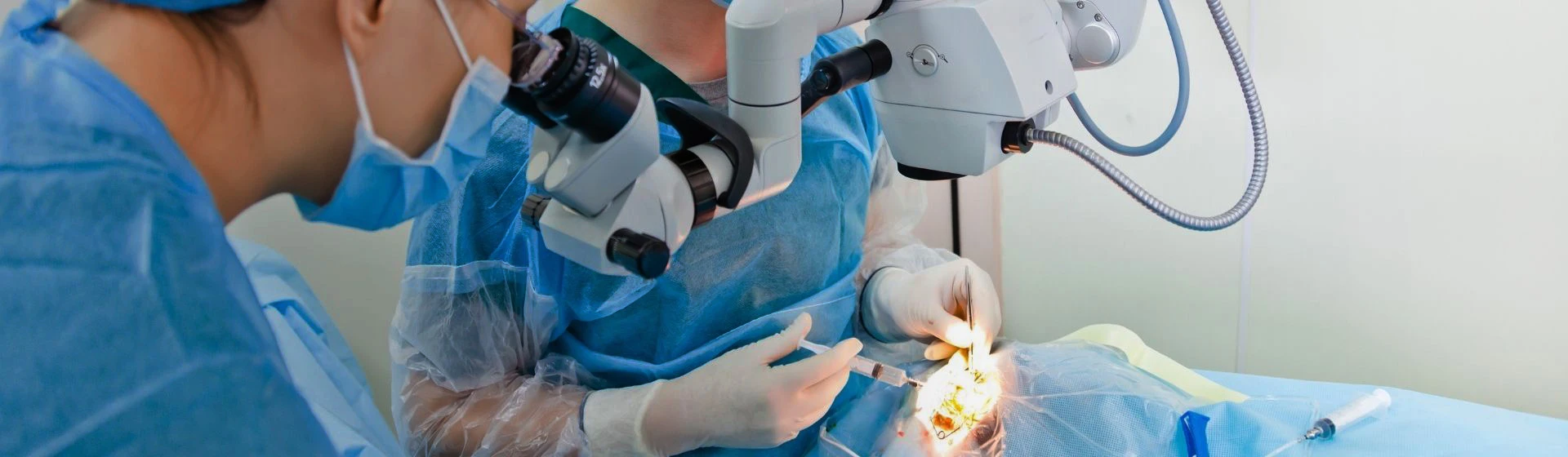
The choice of treatment depends on the location, size, and presence of complications. Only surgical treatment guarantees complete recovery and reduces the risk of recurrence.
There are the following methods:
Used for small asymptomatic cysts
Temporary solution, does not eliminate the cause
Administration of substances to destroy the cyst capsule
Radical method, which involves removing the salivary gland cyst along with its membrane
Indications for removal of salivary glands are:
the cyst is large or rapidly growing;
the formation causes discomfort, speech, chewing, swallowing disorders;
there are relapses after punctures or sclerotherapy;
retention cysts with a tendency to suppuration have been diagnosed;
the formation has become infected, pus or pain has appeared;
there is a suspicion of tumor origin.
A cyst of the parotid gland requires special attention. In such cases, surgery is necessary, as the formation can compress the facial nerve.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient or inpatient basis, depending on the complexity.
Main stages:
Anesthesia — local or general anesthesia.
Dissection of the mucous membrane or skin (depending on the location of the cyst).
Careful removal of the formation together with the capsule.
If necessary — partial or complete removal of the affected salivary gland.
Suture application.
With a sublingual location of the ranula, the operation involves excision of the cyst through the oral cavity. If a minor salivary gland cyst is diagnosed, removal is performed through a small incision without significant intervention.

Postoperative recovery lasts from several days to 2-3 weeks.
Recommendations for patients:
observing oral hygiene;
temporary restriction of solid and hot food;
avoidance of physical exertion;
check-ups with a doctor.
Short-term swelling or pain is possible. In most cases, patients return to their usual lifestyle within a few days.
The cost of the procedure depends on:
complexity of the intervention;
type of anesthesia;
need for preliminary diagnostics;
postoperative monitoring.
You can preliminarily familiarize yourself with the prices here. The exact cost is determined by the doctor during the consultation after the examination and diagnosis. Make an appointment at a time convenient for you and get individual recommendations.
In some cases, small cysts, especially retention cysts, may shrink or even temporarily disappear. However, they most often reappear. Complete elimination is possible only after surgical removal. This is especially true in situations where the cyst causes discomfort or is prone to complications.