Lichen planus treatment
Lichen treatment in Kyiv
Lichen is not a single disease, but rather a group of contagious fungal and viral conditions that manifest as red, pink, or gray patches on the skin. Any form of lichen spreads quickly to other areas of the body and is easily transmitted to others.
Types and causes of lichen
A wide variety of diseases are commonly referred to as “lichen,” some of which (for example, psoriasis) are non-contagious. The most common types include:
-
Gibert’s pink lichen;
-
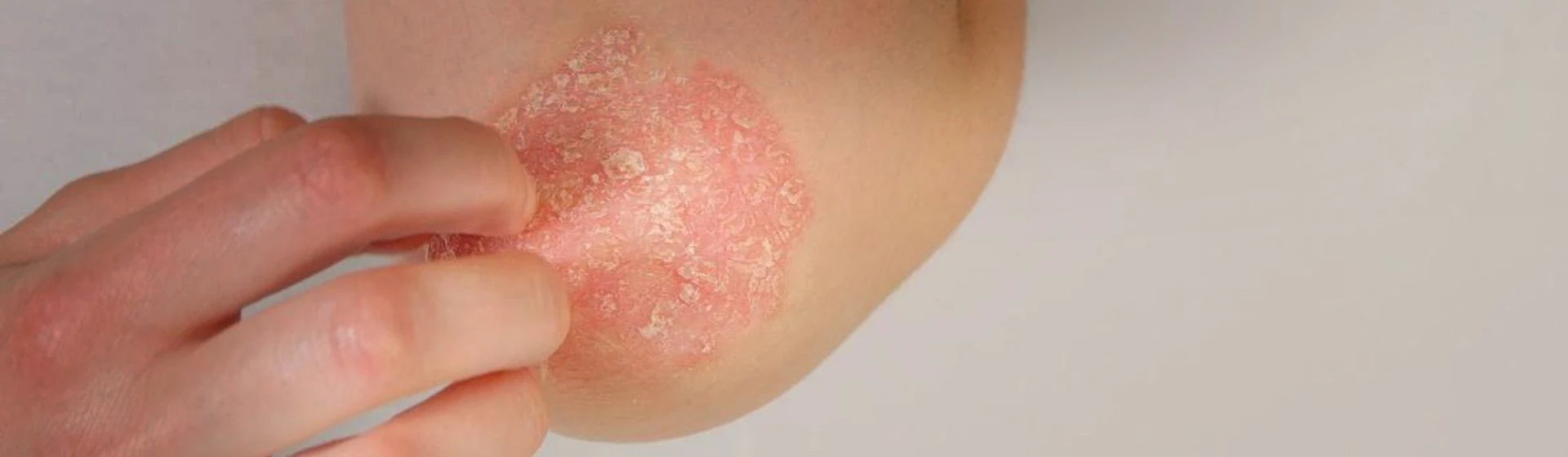
scaly lichen (psoriasis);
-
red flat lichen;
-
pityriasis versicolor (multicolored lichen);
-
herpes zoster (shingles);
-
weeping lichen (eczema);
-
ringworm, and others.
Contagious types of lichen, such as ringworm, can be transmitted from animals or other people. Contributing factors to infection include:
-
poor personal hygiene;
-
wearing other people's clothing;
-
skin injuries;
-
weakened immune system.
Non-contagious conditions also sometimes referred to as lichen (such as eczema or psoriasis) may be caused by metabolic disorders, inherited predispositions, stress, or the aggressive influence of the environment. These causes are called disease triggers or initiating factors.
Symptoms of lichen
In the case of contagious forms, it may take several days to weeks from the moment of infection for symptoms to appear. Non-contagious types of lichen do not develop until the body is exposed to a trigger.
Lichen symptoms are quite similar, which is why only a dermatologist can determine the exact type and whether it is contagious. Lichen usually presents as:
-
oval rashes in the form of fluid-filled blisters;
-
red, whitish, or gray patches;
-
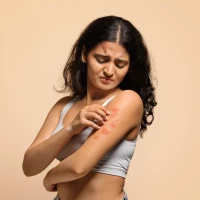
itching in the affected skin area;
-
flaking.
In some cases, fever and headaches may occur.
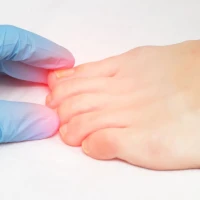
Rashes most commonly appear on the abdomen, back, arms, and legs. Lichen can also develop in areas of scratching, increased sweating, or skin damage. Patch sizes may reach several centimeters, and in advanced cases, they may merge and become very itchy. If lichen affects the scalp, hair loss is possible.
Lichen treatment
Many people try to treat lichen on their own, blindly using various ointments and medications. As a result, it is not uncommon for patients to mistakenly treat herpes zoster (caused by a virus), psoriasis, or eczema with antifungal medications. Naturally, such treatment is ineffective and may even be harmful.
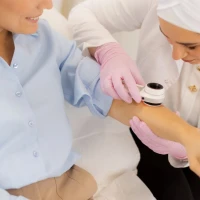
How can you determine the specific type of lichen you have? First of all, consult a qualified dermatologist for an examination. During the appointment, the doctor will inspect the affected areas and, if necessary, prescribe additional tests, such as a skin scraping for fungal infection. If psoriasis or eczema is suspected, a comprehensive diagnostic approach is required to identify and eliminate disease triggers.
Based on the examination and test results, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and only then prescribe treatment, which may include antifungal, antiviral, antihistamine, and other medications. To accelerate recovery, vitamin complexes, ozone therapy, and other restorative procedures may also be recommended.
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist by phone or by filling out the form on the website.
Our doctors




Let's take care
about your health: