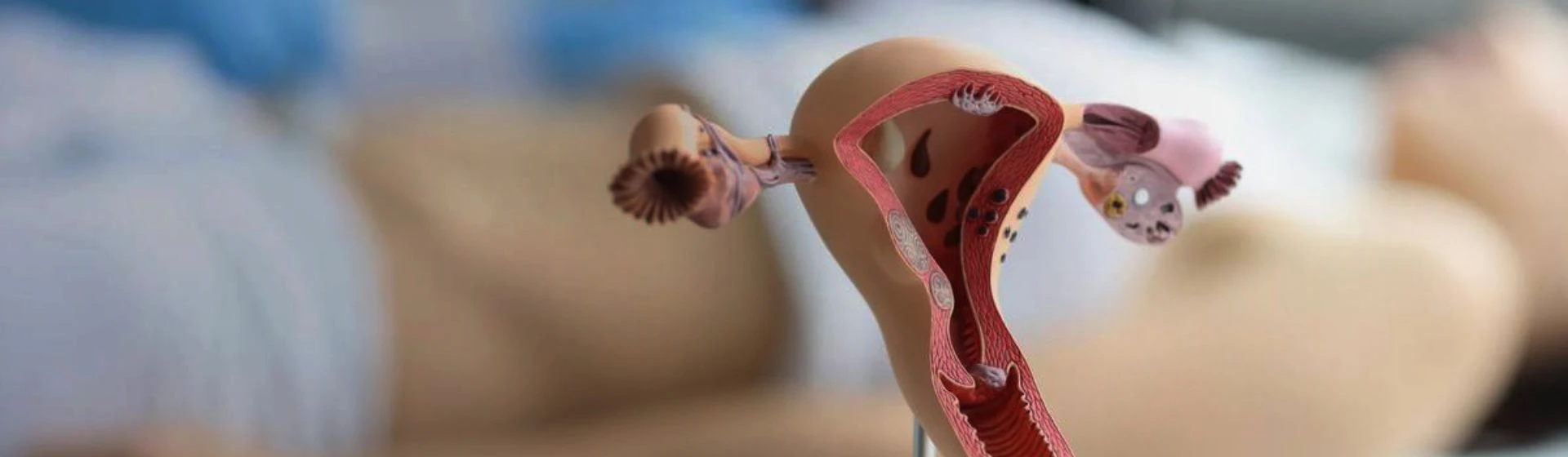
The laparotomic method involves open access to the pelvic organs through a larger incision in the abdominal cavity. This method is used in cases where laparoscopy is impossible or ineffective, for example, in the case of large tumors or complications of infectious diseases.
The main stages of open adnexectomy:
1. Anesthesia. Like laparoscopic surgery, laparotomy is performed under general anesthesia.
2. Access to the pelvic organs. After anesthesia is administered, the doctor prepares the operating field and makes an incision in the lower abdomen. Typically, the incision can reach from 10 to 20 cm.
3. Removal process. During laparotomic adnexectomy, the fallopian tubes and, if necessary, the ovaries are removed more radically, but with full control over each stage of the operation. This is especially important in complex cases when it is necessary to preserve the integrity of neighboring tissues or avoid the spread of infection.
4. Closing the surgical field. After the removal of the affected organs is completed, the doctor sutures the incision. If necessary, a drain is left to prevent fluid accumulation in the postoperative period.
Advantages of the laparotomic technique:
-
Reliable access to organs - the open method allows the surgeon to have greater control over the surgical field, which is important in complex cases.
-
Effectiveness in large tumors - Laparotomy is the preferred method for advanced forms of infectious diseases, as well as when it is necessary to remove large tumors.
Disadvantages of the laparotomic technique
-
Greater postoperative discomfort – due to the large incision, the patient experiences more pain after the operation.
-
Longer recovery period – recovery after laparotomy can take up to 4-6 weeks.
-
Cosmetic aspect – the incision usually leaves a noticeable scar.