No, psoriasis is not an infectious disease and cannot be transmitted from person to person. Skin contact, sharing household items, or being close to someone with psoriasis is completely safe.

Psoriasis treatment
Psoriasis is a very common dermatological condition. It manifests through itching, the formation of inflammatory rashes, and skin flaking. Around 4% of the world’s population suffers from psoriasis. Experts note that the earlier the signs of psoriasis appear, the more severe the disease course is likely to be. The cause of psoriasis is the hyperactive growth of skin cells, which leads to the formation of plaques. Psoriasis can be chronic (with possible flare-ups) or relapsing. Contrary to a widespread misconception, psoriasis is not contagious. If you’ve been diagnosed with psoriasis and have undergone multiple courses of treatment without results, don’t lose hope! Quite often, experienced doctors disprove the diagnosis and, based on clinical tests, identify the true cause of the symptoms in other body systems.
What causes psoriasis?
Most commonly, the condition is triggered by:
-
Stress, fatigue, and nervous system exhaustion;
-
Weakened immunity;
-
Various endocrine disorders;
-
Infectious diseases, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections;
-
Genetic abnormalities;
-
Body intoxication;
-
Injuries and skin damage;
-
Unbalanced diet;
-
Harmful habits;
Lifestyle factors play an important role in the course of the disease. In particular, smoking in patients with psoriasis is considered a factor that may worsen skin condition, contribute to more frequent flare-ups, and reduce the effectiveness of therapy.
Symptoms of psoriasis
Psoriasis presents with the following symptoms:
-
Eruptions in the form of round red or pink nodules that form plaques covered with silvery scales;
-
Itching in hairy areas, as well as on the knees and elbows;
-
Pain in the right side and lower back;
-
Bitter taste in the mouth;
-
Fatigue, muscle weakness.
In addition to rashes and scaling, many patients with psoriasis experience dry skin, which is accompanied by a feeling of tightness, the appearance of cracks, and increased discomfort, especially during the cold season.
Types of psoriasis
Depending on clinical manifestations, the following types of psoriasis are distinguished:
- Guttate psoriasis – an acute form of the disease that most commonly develops after a streptococcal infection in children and adolescents. It appears as numerous bright red eruptions in the form of papules with slight flaking.
- Plaque (vulgar) psoriasis – primarily develops on the scalp, under the knees, around the elbows, lower back, and sacrum. It appears as papular pink-red eruptions that initially have well-defined edges, but may merge into large spots over time. This form also features plaques covered with light scales.
- Generalized pustular psoriasis – occurs in three forms. The most common is Barber’s pustular psoriasis, characterized by well-defined plaques with pustules around them on the palms and soles. The second form is Allopo’s acrodermatitis, which includes vesicles, pustules, and scaly-erythematous spots on the fingers and toes. The third form is Zumbusch psoriasis, which includes rashes along with severe fever and general malaise.
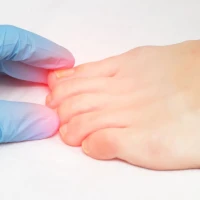
- Psoriatic arthritis – accompanied by simultaneous skin rashes and joint involvement. This is characterized by limited joint mobility, pain when bending, swelling, and redness of the skin. In some cases, it leads to joint deformity.
Psoriatic eruptions can appear anywhere on the body, but most commonly affect:
-
Scalp;
-
Sacral area;
-
Elbow and knee joints;
-
Face;
-
Large skin folds;
-
Genital area;
-
Palms;
-
Soles;
-
Nails.
Depending on the affected area, psoriasis is categorized as palmoplantar, genital, facial, etc.
If eruptions cover less than 20% of the skin, psoriasis is considered limited; if more than 20%, it is widespread; and if almost the entire skin is affected, it is referred to as universal.
How is psoriasis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in order to determine the form and stage of psoriasis. The common form of psoriasis is characterized by the formation of flat, reddish plaques covered with white-silvery scales. In the exudative form of the disease, grayish-yellow scales appear on psoriatic plaques. The development of the most severe forms of psoriasis may occur at the onset of the disease or at later stages due to unfavorable factors or as a result of irrational treatment.
Nail psoriasis is a common manifestation of the disease and may be observed even in the presence of minimal skin lesions. This condition is characterized by thickening of the nail plates, the appearance of pinpoint depressions, changes in nail color, and separation of the nail from the nail bed, which requires differential diagnosis with fungal infections.
To уточнення the diagnosis and assess disease activity, a dermatologist applies a comprehensive approach that may include laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods. If necessary, additional examinations are performed to differentiate psoriasis from other dermatological conditions and to determine the optimal treatment strategy.
Psoriasis treatment
Topical treatment methods depend on the stage and form of the disease. For the progressive stage (new bright red nodules appear, merging into plaques), the following are used:
-
Emollients and keratoplastic agents in moderate concentrations;
-
Ointments, creams, and lotions containing glucocorticoids;
-
Preparations with activated zinc pyrithione.
For the stationary stage (no increase in lesion areas) and regressive stage (lesions fade, flaking reduces), the following are used:
-
Ointments with vitamin D3 analogues;
-
Ointments containing tar, naphthalan, and hydroxyanthrones.
If more than 20% of the skin surface is affected, or in severe forms of psoriasis, or when topical treatment is ineffective, systemic therapy is prescribed. This includes hyposensitizing, rheocorrective, and detoxifying therapy.
Modern pharmacological treatment includes:
-
Cytostatics with a pronounced effect;
-
Synthetic retinoids;
-
Glucocorticoids (when other drugs are ineffective).
Non-pharmacological treatment involves systemic photochemotherapy — ultraviolet irradiation with a wavelength of 320–400 nm combined with photosensitizing agents.
Psoriasis flare-ups: causes and manifestations
Psoriasis has a chronic course with periods of relative symptom remission and flare-ups. During an exacerbation, new skin lesions may appear, the affected skin area can increase, and scaling and itching often become more pronounced. In some patients, general well-being may worsen, accompanied by increased fatigue and discomfort.
Factors that most commonly trigger psoriasis flare-ups include psycho-emotional stress, infectious diseases, hormonal fluctuations, non-adherence to treatment regimens, skin trauma, and unfavorable environmental conditions. Timely adjustment of therapy helps reduce symptom severity and shorten the duration of flare-ups.
Possible complications of psoriasis
With prolonged or poorly controlled disease, psoriasis may be associated with the development of complications. One of the most common is psoriatic arthritis, which is characterized by joint involvement, pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Persistent changes in the skin and nails may also occur and can remain even during periods of remission.
In addition to skin and joint manifestations, psoriasis can negatively affect a patient’s quality of life, leading to emotional distress and social difficulties. Therefore, regular follow-up with a dermatologist, adherence to medical recommendations, and timely treatment aimed at disease control and prevention of possible complications are essential.
Private clinic services in Kyiv: the cost of psoriasis treatment at the “Oxford Medical”
Psoriasis treatment requires a comprehensive and individualized approach that takes into account the form of the disease, the stage of its course, the extent of skin involvement, and the patient’s overall health. These factors determine the treatment strategy and influence the cost of therapy. At the private clinic “Oxford Medical,” treatment programs are developed after an in-person consultation with a dermatologist and the necessary diagnostic evaluations.
You can review the prices for consultations and services in advance in the relevant section of the website.
If you are looking for professional medical services in Kyiv, you can schedule a consultation at a convenient time by phone or via the online form on the website.
Frequently asked questions
Is psoriasis contagious?
Why does psoriasis occur?
Psoriasis is associated with dysfunctions of the immune system that lead to an accelerated turnover of skin cells. Genetic predisposition, stress, hormonal imbalances, infections, and unfavorable environmental factors may play a significant role in triggering the disease.
Can psoriasis be cured permanently?
At present, psoriasis is considered a chronic condition that cannot be completely cured. However, modern treatment approaches make it possible to achieve long-term remission, reduce symptom severity, and improve patients’ quality of life.
Why is psoriasis considered incurable?
Psoriasis has a complex, multifactorial pathogenesis involving genetic and immune-related mechanisms. Since these processes cannot be fully eliminated, treatment is aimed at symptom control, reducing the frequency of flare-ups, and maintaining stable skin condition.
Which diseases can resemble psoriasis?
In terms of clinical presentation, psoriasis may resemble seborrheic dermatitis, eczema, lichen planus, fungal skin infections, or atopic dermatitis. Therefore, an accurate diagnosis requires evaluation by a dermatologist and, if necessary, additional diagnostic tests.
Our doctors





Let's take care
about your health:






