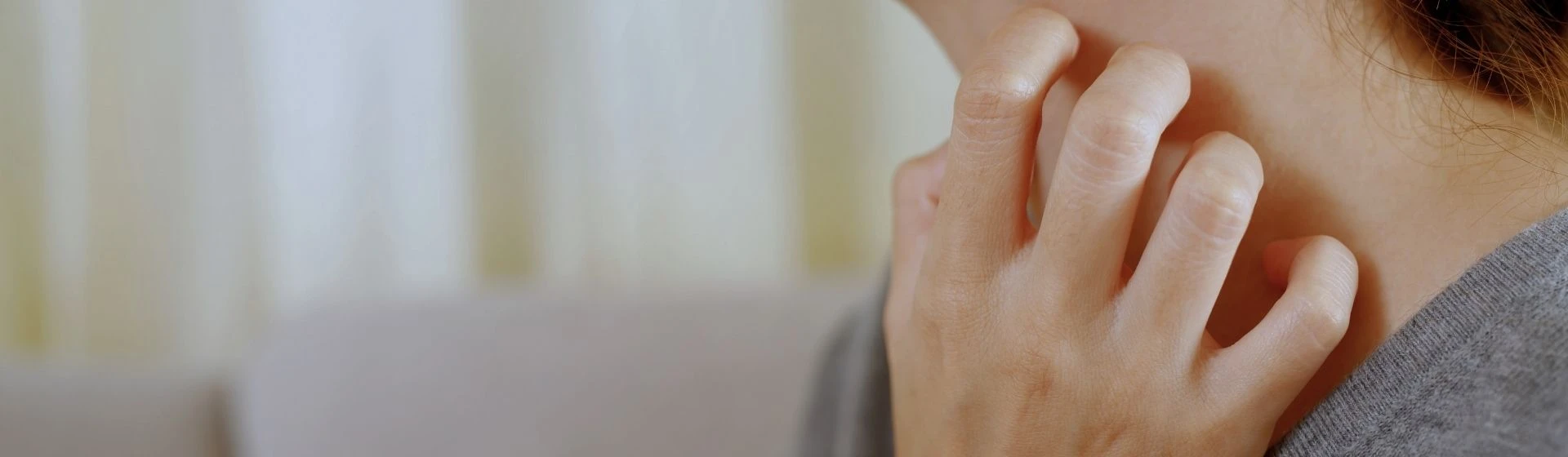
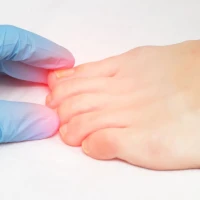
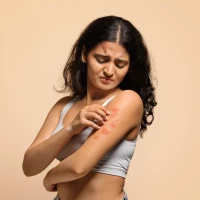
Allergic dermatitis presents with redness, swelling, and itching of the skin. Allergic spots on the skin, small nodules, or blisters may appear, sometimes accompanied by oozing. The rash usually occurs at the site of contact with the allergen and may gradually spread.

Treatment of allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis is a skin condition that occurs due to a hypersensitive (allergic) reaction of the human body to a specific type of irritant. This condition is diagnosed by allergists using classical allergy tests. Quite often, a condition such as allergic dermatitis is associated with the workplace. For example, medical workers may experience latex allergy, others may react to chemical reagents, animal hair, etc. The cause of allergic dermatitis is often found at home — in household chemicals, synthetic clothing, low-quality cosmetics, and even children's toys.
Typically, allergic dermatitis develops rather slowly: the allergy arises after prolonged contact of the person with the allergen. The condition manifests at the site and time of contact with the allergen, causing redness, swelling, papules, and vesicles. If contact with the allergen is not stopped in time, allergic dermatitis progresses and can develop into eczema — a more severe condition to treat.
Allergic dermatitis: causes
Essentially, allergic dermatitis is a delayed-type allergic reaction, mainly involving lymphocytes. In such cases, allergens are often various chemical compounds — chromium, nickel, insecticides, substances found in laundry detergents, and so on. A significant number of allergens are found in medications and cosmetics: antibacterial ointments, hair dyes, etc. Due to their small size, allergens usually do not cause allergies by themselves, as immune cells of the body cannot recognize them. However, once in the bloodstream, they bind to large blood proteins. These compounds act as allergens.
Symptoms of allergic dermatitis
The process of an excessive immune response typically starts a few days before the first symptoms appear.
The first signs of allergic dermatitis:
-
noticeable redness of the skin;
-
pronounced swelling;
-
allergic rash on the face;
-
intense itching at the contact site;
-
appearance of weeping areas and ulcers.
The combination of several symptoms is a reason to consult a dermatologist in a timely manner, as early diagnosis and elimination of contact with the allergen can prevent the progression of the disease and the development of complications.
Classification of Allergic Dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis belongs to diseases that develop through a delayed-type hypersensitivity mechanism (type IV hypersensitivity). The inflammatory process forms after repeated contact of the skin with an allergen and does not occur immediately, but develops over several days.
Further classification of the disease is carried out according to the conditions of occurrence and the course of the disease, which is of practical importance for choosing treatment tactics.
According to the conditions of occurrence:
- household allergic dermatitis — develops as a result of skin contact with allergens in everyday life, including household chemicals, cosmetics, metals, synthetic materials, or detergents;
- occupational allergic dermatitis — occurs due to regular or prolonged contact with allergens in the workplace, such as chemicals, latex, dyes, medications, or industrial compounds.
According to the course of the disease:
- acute allergic dermatitis — characterized by the sudden appearance of redness, swelling, itching, and rashes after contact with an allergen;
- chronic allergic dermatitis — develops with prolonged or repeated exposure to the allergen and is accompanied by persistent inflammation, dryness, skin thickening, and periodic exacerbations.
According to the localization of lesions:
- allergic dermatitis on the hands;
- allergic dermatitis on the face;
- allergic dermatitis on the legs and other areas of the skin.
This classification makes it possible to properly assess the course of the disease and select effective treatment, taking into account the causes and clinical manifestations
Consequences of Allergic Dermatitis
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, allergic dermatitis may lead to complications associated with prolonged inflammation and impairment of the skin’s barrier function. Persistent itching and scratching of affected areas contribute to damage to the skin, creating conditions for secondary bacterial or fungal infection.
With a prolonged course of the disease, lichenification may develop — thickening of the skin with accentuation of the skin pattern — as well as oozing and cracking, which complicate healing and increase the risk of infection. Chronic inflammation may also be accompanied by changes in skin pigmentation after the resolution of acute manifestations.
In some cases, allergic dermatitis becomes chronic with periodic exacerbations or transforms into eczema, which significantly complicates further treatment. A long disease course and cosmetic manifestations, especially on exposed areas of the body, may negatively affect a patient’s daily life, causing physical and psychological discomfort.
Diagnosis
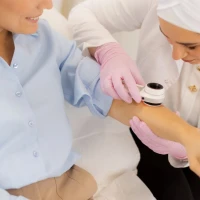
When diagnosing the condition, the allergist first rules out other diseases with similar symptoms: eczema, toxicoderma, and others. Usually, the diagnosis is not difficult based on the data obtained during the patient interview and skin examination. To confirm the diagnosis, skin allergy tests are widely used today. These methods help the doctor confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific allergens that triggered the allergic dermatitis.
Cutaneous Allergic Dermatitis: Treatment
The effectiveness of allergic dermatitis treatment depends on correctly identifying the cause of the disease and timely elimination of contact with the allergen. Discontinuing exposure to the irritant is the basis for reducing inflammation and preventing recurrent flare-ups.
Treatment for allergic dermatitis is selected individually and may include medication therapy aimed at reducing inflammation, itching, and restoring the protective properties of the skin. Treatment of allergic dermatitis in adults is carried out taking into account the extent of skin involvement, the duration of the disease, and the presence of comorbid conditions that may affect skin reactivity.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis on the face requires a special approach, as the skin in this area is thinner and more sensitive to external influences. In such cases, therapy involves the use of gentle products that allow control of inflammation without the risk of additional irritation.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis on the legs also has its own characteristics, in particular due to slower skin recovery and the possible effect of friction from clothing or footwear, which requires a carefully selected treatment regimen.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis is not limited to eliminating external manifestations alone. Therapy is aimed at stabilizing the condition of the skin, reducing its reactivity, and preventing recurrent exacerbations, which makes it possible to achieve long-term disease control and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Prevention of Allergic Dermatitis
Prevention of allergic dermatitis is aimed at reducing the risk of skin sensitization and preventing disease exacerbations.
- avoiding contact with known allergens — eliminating or minimizing exposure to substances that have previously caused an allergic reaction;
- careful selection of skincare products and household chemicals — using hypoallergenic products without fragrances or aggressive components;
- protecting the skin when working with irritants — using gloves and other barrier protection when in contact with chemical or occupational allergens;
- regular skin care — maintaining an optimal level of hydration to preserve the skin’s barrier function;
- gentle hygiene practices — avoiding hot water and products that dry out or irritate the skin;
- timely consultation with a doctor — seeing a dermatologist when the first symptoms of an allergic reaction appear in order to prevent complications.
Following these recommendations helps reduce the risk of developing allergic dermatitis and decreases the frequency of its exacerbations.
Services of a Private Clinic in Kyiv: Cost of Treating Allergic Dermatitis at “Oxford Medical”
Treatment of allergic dermatitis requires a comprehensive and individualized approach, taking into account the form of the disease, the duration of its course, the extent of skin involvement, and the patient’s general condition. These factors determine treatment tactics and affect the cost of therapy. At the private clinic “Oxford Medical,” the treatment program is selected after an in-person consultation with a dermatologist and the necessary diagnostic evaluation.
You can ознакомиться with the prices for consultations and services in the relevant section of the website.
If you need high-quality medical services in Kyiv, you can book an appointment at a convenient time by phone or via the online form on the website.
Frequently asked questions
What does allergic dermatitis look like?
What can cause allergic dermatitis?
The disease develops as a result of contact with substances to which the body has increased sensitivity. Most often these include household chemicals, cosmetics, metals, latex, medications, or occupational irritants. The reaction does not occur immediately but develops after repeated contact.
Why is allergic dermatitis dangerous?
Without treatment, allergic dermatitis can become chronic, be complicated by infections, and lead to persistent skin changes. Prolonged inflammation increases the risk of skin thickening, pigmentation disorders, and the development of eczema, especially with frequent exacerbations.
Can you wash when you have allergic dermatitis?
Hygienic procedures are allowed, but with certain limitations. It is recommended to use warm water and mild hypoallergenic products without fragrances. When exposed areas are affected, particularly when allergic rashes appear on the face, aggressive cleansing should be avoided.
Our doctors





Let's take care
about your health:






